Article by John Miller
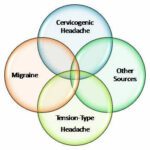
Causes of Cervicogenic Headaches
Musculoskeletal and neurovascular structures in the neck play a significant role in causing cervicogenic headaches. Here are some key factors that actively contribute to the development of these headaches:
Upper Neck Joint Dysfunction
The dysfunction of the upper three neck joints, which include the atlantooccipital joint (O-C1), atlantoaxial joint (C1/2), and C2/3 cervical spine joints, actively causes cervicogenic headaches. When these joints become too stiff, excessively mobile, or locked in an abnormal position, they actively generate pain signals. These signals are then actively transmitted to the brainstem's trigeminocervical nucleus (TCN). As a result, the brain actively interprets these signals as a headache.
Neck Muscle Involvement
Active overworking, knots, spasms, and weakness in the neck and shoulder blade muscles actively contribute to cervicogenic headaches. In certain cases, overworked muscles actively attempt to protect injured neck joints. Conversely, weak muscles actively contribute to muscle fatigue-related symptoms. It is crucial to actively maintain proper resting tension, length, strength, power, and endurance in the neck muscles to actively prevent cervicogenic headaches.
Cervical and Occipital Nerve Irritation
Arthritis, disc bulges, or swelling actively cause pinching of the nerves in the upper neck. These conditions actively occur. As a result, this irritation actively leads to abnormal neural motion, known as neuromechanosensitivity or abnormal neurodynamics. Consequently, pain signals actively get transmitted along the nerves, causing headaches. To illustrate, envision the neck as the "switch," the nerves as the "power cords," and the headache as the "light" that actively comes on.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Consulting with a skilled physiotherapist or headache specialist actively plays a crucial role in obtaining an accurate diagnosis and receiving appropriate treatment for cervicogenic headaches. They actively possess the ability to assess and address the dysfunction in the neck joints, muscles, and nerves that actively contribute to the occurrence of headaches.
The treatment for cervicogenic headaches may actively involve a combination of manual therapy techniques, targeted exercises to improve muscle imbalances, correction of posture, implementation of pain management strategies, and recommendations for lifestyle modifications aimed at reducing triggers and promoting overall neck health. Furthermore, by actively addressing the underlying causes and optimising the function of the neck structures, individuals can actively experience significant relief from cervicogenic headaches and considerably enhance their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Dysfunctions in the musculoskeletal and neurovascular structures of the neck actively result in cervicogenic headaches. These dysfunctions actively involve the upper neck joints, neck muscles, and cervical and occipital nerves. It is actively essential to understand the causes of cervicogenic headaches for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Actively seeking the advice of a qualified physiotherapist with a particular interest in headaches is crucial for actively assessing and managing cervicogenic headaches. Through a comprehensive evaluation, they can actively identify specific dysfunctions and actively develop a personalised treatment plan to address them.
The treatment plan for cervicogenic headaches may actively involve employing manual therapy, implementing targeted exercises, correcting posture, and implementing pain management strategies. By actively addressing the underlying causes of these headaches and actively improving the function of the neck structures, individuals can actively find relief.. Additionally, it is actively crucial to prioritise neck health and actively adopt appropriate lifestyle modifications to effectively reduce triggers and actively prevent future occurrences of cervicogenic headaches.
Remember, if you actively experience persistent or severe headaches, we actively recommend you consult a healthcare professional to actively ensure an accurate diagnosis and actively receive appropriate treatment.