De Quervains Tenosynovitis
What is De Quervains Tenosynovitis?
De Quervains tenosynovitis, a common wrist and thumb condition, primarily affects the abductor pollicis longus (APL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) tendons. These tendons pass through a tunnel near the radius bone’s end in the forearm, lined with a slippery substance called tenosynovium. Inflammation or thickening in this area leads to pain and limited movement.
What is the Cause of de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis?
This condition often stems from repetitive occupational hand and thumb movements, such as pinching, grasping, or wringing. These actions can inflame the tenosynovium and tendons, leading to swelling and restricted movement. Injury-induced scar tissue, rheumatoid arthritis, hormonal changes, and certain conditions like diabetes and thyroid disease also contribute to its development.
Recognising Symptoms
The initial symptom is soreness on the thumb side of the forearm, near the wrist. Untreated, it can spread up the forearm or down into the wrist and thumb. Swelling, a creaking noise (crepitus) during tendon movement, and difficulty in grasping are common signs. A lump at the thumb’s base may also form.
Diagnosis Techniques
Diagnosis primarily relies on symptoms and a physical exam. The Finkelstein test is a key diagnostic tool, best performed by a healthcare professional. Imaging is typically unnecessary.

What is the Best Treatment for de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis?
Treatment includes rest, splinting, physiotherapy, and possibly glucocorticoid injections.
Rest and Movement Modification:
Avoiding painful activities and maintaining neutral wrist alignment are crucial.
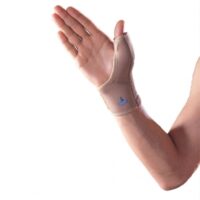
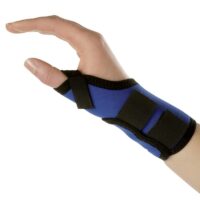
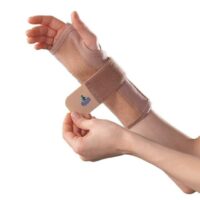
Thumb-Spica Splint:
This helps immobilise the wrist and thumb, aiding in healing. View splints here: Thumb-Spica Splint
Glucocorticoid Injections:
These can provide relief, especially when combined with splinting.
Physiotherapy:
Focuses on reducing tendon irritation. This includes ergonomic advice, ice packs, soft-tissue massage, stretching, and strengthening exercises. Therapists also suggest changes in work or activity techniques to reduce stress on the thumb and wrist.
Will de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis Go Away on its Own?
New Research and Developments
Recent advancements in physiotherapy emphasise the importance of early intervention and customised treatment plans. Techniques like ergonomic analysis and targeted exercises have shown promising results in speeding up recovery and reducing recurrence rates. Additionally, ongoing research is exploring the role of diet and supplements in managing inflammation and promoting tendon health.
What to Do? Seek Professional Advice
If you suspect you have De Quervains tenosynovitis, consult a physiotherapist or doctor. They will assess your condition, suggest appropriate treatments, and guide you through a personalised recovery plan. Remember, early diagnosis and tailored care are key to effective recovery and preventing long-term issues.
Conclusion
De Quervains tenosynovitis, while painful, is highly treatable with the right approach. Understanding the condition, early intervention, and following a physiotherapist’s guidance are vital for a quick and successful recovery. By adjusting daily habits and incorporating specific exercises, you can manage symptoms and prevent future occurrences. Stay informed, stay active, and don’t hesitate to seek professional advice for optimal wrist and thumb health.
For specific advice regarding your de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, please consult your hand physiotherapist or doctor.
Related Articles
- Thumb Pain: Offers information on causes and treatment of thumb pain, closely related to De Quervains Tenosynovitis.
- Hand & Wrist Injuries: Provides a comprehensive overview of common hand and wrist injuries, including symptoms and treatments.
- Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI): Discusses RSI, a condition related to repetitive hand and wrist movements, much like De Quervains Tenosynovitis.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Explores rheumatoid arthritis, a condition mentioned as a contributing factor to De Quervains Tenosynovitis.
- Ergonomic Assessments: Explains ergonomic assessments which can help prevent conditions like De Quervains Tenosynovitis.
- Physiotherapy Treatments: Outlines various physiotherapy treatments, relevant for De Quervains Tenosynovitis recovery.