Swimmers Back: Navigating Back Pain in the Pool
Introduction
Swimming, while an excellent form of exercise, can lead to back pain, commonly referred to as “Swimmer’s Back.” This condition, particularly prevalent among butterfly and breaststroke swimmers, warrants understanding and proper management.
Understanding Swimmer’s Back Pain
Swimmer’s Back arises from the spinal stresses unique to swimming, especially in strokes like butterfly and breaststroke. These movements can cause significant strain on the lower back.

Conditions Associated with Swimmer’s Back
Swimmer’s Back is often linked with several specific spinal conditions:
- Spondylolysis: This condition involves a stress fracture in one of the vertebrae in the lower back. It’s common in athletes who engage in sports involving repetitive bending and twisting.
- Spondylolisthesis: This occurs when a vertebra slips forward over the bone below it. It’s often a progression from spondylolysis and can cause lower back pain.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: With this condition, the intervertebral discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae, start to degenerate, leading to pain and discomfort.
Understanding these conditions and their implications is crucial for swimmers, as they can affect performance and overall spinal health. Preventive measures and appropriate treatments are key to managing these conditions effectively. For more information, it’s beneficial to consult articles specifically addressing:
Prevention Strategies for Swimmer’s Back
To prevent Swimmer’s Back, several key strategies are effective:
- Proper Technique: Mastering correct swimming techniques is vital. This includes understanding the mechanics of different strokes and ensuring body alignment and movement minimise stress on the back.
- Strength and Flexibility: Building core strength and enhancing hip flexibility are crucial. A strong core supports the lower back, reducing the risk of injury, while flexible hips allow for smoother, more efficient movements in the water.
- Physiotherapy Assessments: Regular check-ups with a physiotherapist are recommended. These assessments can provide personalised advice, help in identifying potential issues early, and guide in maintaining optimal spinal health through swimming.
Treatment Approaches for Swimmer’s Back
Effective management of Swimmer’s Back encompasses several key strategies:
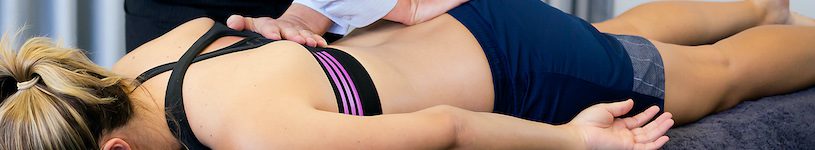
- Physiotherapy: This involves customised exercises and manual therapy tailored to the individual’s needs. Exercises often focus on strengthening the core and improving flexibility, while manual therapy might include techniques like massage and mobilisation to alleviate pain and improve function.
- Rest and Recovery: It’s crucial for swimmers to allow sufficient recovery time after intense training sessions. This includes both physical rest and methods like ice or heat therapy, which can help in reducing inflammation and promoting muscle relaxation.
- Training Modifications: Adjusting training routines is essential to reduce back strain. This might involve altering stroke techniques, reducing training intensity, or incorporating cross-training activities to balance muscle use and prevent overuse injuries.
These approaches, combined, offer a holistic path to managing and recovering from Swimmer’s Back, emphasising not just treatment but also prevention and ongoing care.
The Role of Research
Latest research emphasises core stability exercises and hip flexor stretches in preventing and managing back pain in swimmers.
When to Seek Professional Advice
Experiencing back pain while swimming should prompt a consultation with a physiotherapist for a comprehensive assessment and tailored treatment plan.
Conclusion
Managing and preventing Swimmer’s Back requires attention to technique, strength, and flexibility. Professional guidance is key to enjoying swimming while minimising injury risks.
What to Do?
If you’re experiencing discomfort or pain while swimming, it’s vital to seek a physiotherapist’s assessment for appropriate guidance and treatment.
For further insights, consider exploring additional resources on PhysioWorks, such as information on swimming-related injuries and sports physiotherapy.