Sciatica
Article by John Miller
Managing Sciatica Pain
Sciatica involves discomfort linked to the sciatic nerve, often discussed in the context of back pain. This comprehensive guide aims to clarify the nature of sciatica, pinpointing its causes, symptoms, and various treatment strategies. With practical, evidence-backed advice, it seeks to assist those grappling with sciatica on their path to recovery.

What is Sciatica?
The sciatic nerve, originating from spinal segments L4 to S3, is the longest in the human body. It extends from the lower back through the buttocks and down the legs. Sciatica denotes pain along this nerve’s pathway, usually due to irritation or compression. The condition’s complexity can lead to misdiagnosis and ineffective treatments.
Common Causes and Symptoms
Sciatica is commonly triggered by a herniated disc pressing against the sciatic nerve. Other factors include joint inflammation, lumbar spondylosis, spondylolisthesis, piriformis syndrome, and spinal stenosis. Symptoms range from lower back pain radiating to the legs to tingling, numbness, or muscle weakness. Timely medical intervention is crucial to prevent permanent nerve damage.
Bulging Disc and Its Role in Sciatica
A bulging disc occurs when the soft gel-like centre of a spinal disc protrudes through a weakness in the outer layer. This can press against the sciatic nerve, causing sciatica pain. Symptoms often include lower back pain, leg pain, and, in some cases, numbness or weakness in the affected leg. Understanding the mechanics of a bulging disc is crucial for targeted sciatica treatment. Specific exercises and physiotherapy can alleviate pressure on the nerve.
Lumbar Facet Joint and Sciatica Pain
The lumbar facet joints, located at each segment of the spine in the lower back, play a significant role in stability and flexibility. When these joints become arthritic or suffer wear and tear, they can contribute to sciatica symptoms by irritating nearby nerve roots. Treatment may include physiotherapy, manual therapy, and lifestyle modifications to reduce joint inflammation and prevent further irritation of the sciatic nerve.
Piriformis Syndrome: A Unique Cause of Sciatica
Piriformis syndrome involves the piriformis muscle—a small muscle deep in the buttocks—irritating or compressing the sciatic nerve. This leads to sciatica-like pain, tingling, and numbness in the back of the leg. Addressing piriformis syndrome requires stretching, strengthening exercises, and possibly manual therapy techniques to relieve muscle tightness and reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Degenerative Disc Disease and Its Impact on Sciatica
Degenerative disc disease, a condition stemming from the natural aging process, can significantly contribute to sciatica symptoms. As discs degenerate, they lose their cushioning ability, leading to decreased disc height and potential disc herniation, which can irritate or compress the sciatic nerve. Symptoms may include chronic lower back pain radiating to the legs, and severe pain upon moving or lifting objects. Managing sciatica involves a combination of physical therapy, pain management strategies, and, in some cases, surgical interventions to address disc damage and relieve nerve compression.
Spinal Stenosis: A Contributing Factor to Sciatica
Spinal stenosis, characterised by the narrowing of spaces within the spine, can exert pressure on the nerves, including the sciatic nerve. This narrowing, often due to age-related changes such as osteoarthritis, can lead to symptoms similar to sciatica, including leg pain, numbness, and weakness. Treatment focuses on relieving pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, often involving physiotherapy exercises designed to improve flexibility and strengthen muscles supporting the spine. In severe cases, surgical options may be considered to widen the spinal canal and alleviate nerve compression.
Diagnosis and Imaging
Diagnosing sciatica involves a thorough physical examination and medical history review, focusing on muscle strength, sensation, and reflexes. Diagnostic imaging, like X-rays or MRIs, may be necessary to pinpoint spinal abnormalities causing nerve distress, particularly affecting the L5 or S1 nerve roots.
Effective Sciatica Treatment Strategies
Treatment for sciatica is tailored to each individual, focusing on the specific reasons behind their condition. This approach incorporates the latest advancements in medicine and physiotherapy, emphasising active, movement-oriented strategies. By identifying the unique factors contributing to each case of sciatica, healthcare professionals can develop a more effective, personalised treatment plan that promotes healing and pain relief.
Exercise and Physiotherapy
Strengthening core and lower back muscles is foundational in treating sciatica, reducing pressure on the sciatic nerve. Flexibility and posture improvement exercises further aid recovery.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Alternating between heat and cold packs can offer immediate pain relief by reducing inflammation and easing muscle tension.
Manual and Alternative Therapies
Manual techniques such as massage and spinal mobilisation, alongside acupuncture and dry needling, can significantly alleviate pain by addressing muscle and spinal alignment issues.
Ergonomic and Lifestyle Adjustments
Making ergonomic changes and adopting a lifestyle that includes regular low-impact exercises like walking or swimming are vital in preventing sciatica recurrence.
Neurogenic Drugs in Sciatica Treatment
Neurogenic drugs play a pivotal role, especially for intense nerve pain. These medications target nerve pain directly, working on the nervous system to alleviate discomfort. They are particularly beneficial for patients whose sciatica pain stems from nerve damage or irritation. By modulating pain signals before they reach the brain, neurogenic drugs can significantly reduce pain intensity, improving quality of life. However, consult a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable neurogenic medication for your situation, as these drugs can have side effects and interactions with other medications.
Advanced and Surgical Interventions
In stubborn cases, exploring advanced treatments such as nerve pain medications, corticosteroid injections, or surgery may be necessary, especially if conservative methods fail to provide relief. Surgery is considered when conservative treatments are ineffective over an extended period, with emergency procedures reserved for severe cases involving significant muscle weakness or loss of bowel or bladder control.
Enjoying Life Again Post-Sciatica
Recovery and Management
Most sciatica cases improve with conservative care, avoiding aggravating activities. Outcomes vary, but approximately 90% of individuals see improvement within six weeks. For persistent pain, engaging in a targeted exercise program is essential.
Exploring Additional Treatment Options
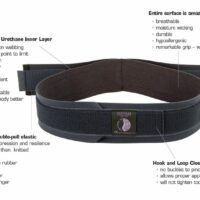
Options like back braces, massage therapy, acupuncture, TENS machines, and posture supports can offer relief and help manage symptoms. Consulting with a physiotherapist for tailored advice is recommended.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Sciatica
Sciatica can significantly impact your life, but a combination of therapies, customised to your specific needs, often provides the most effective relief. If sciatica affects your daily activities, seeking professional advice from a physiotherapist or doctor is a critical first step. They can evaluate your condition, devise a personalised treatment plan, and support you through your recovery journey.
What to Do?
Overcoming sciatica is a personal journey. While this article provides an overview, your path to relief will be unique. Embrace treatments that resonate with your situation, and take the first step towards a pain-free life by consulting a healthcare professional.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: Sandgate

FAQs About Sciatica
- What is the best treatment for sciatica? The best treatment varies but often includes physiotherapy, specific exercises, and sometimes medication or surgery, depending on severity.
- How long does sciatica take to heal? Most cases improve within six weeks with conservative treatment. Persistent cases may require more intensive therapy.
- Can sciatica go away on its own? Yes, many cases resolve on their own with rest and self-care, but professional advice is recommended for persistent pain.
- Is walking good for sciatica? Walking can be beneficial as it helps reduce inflammation and promotes mobility. However, consult a physiotherapist for personalised advice.
- What should you not do with sciatica? Avoid activities that aggravate the pain, such as heavy lifting or prolonged sitting. Focus on gentle movements and exercises.
- Can a physiotherapist help with sciatica? Absolutely. Physiotherapists can provide targeted treatments, exercises, and advice to alleviate sciatica symptoms and promote recovery.
Related Articles
- Herniated Disc Treatment Explains treatments for herniated discs, a common cause of sciatica.
- Piriformis Syndrome Treatment Details treatments for piriformis syndrome, a unique cause of sciatica.
- Spinal Stenosis Therapy Describes therapy options for spinal stenosis, contributing to sciatica.
- Degenerative Disc Disease Management Outlines management strategies for degenerative disc disease and its impact on sciatica.
- Lumbar Facet Joint Pain Discusses how lumbar facet joint issues can lead to sciatica and treatment options.
- Back Pain Relief Provides general advice on relieving back pain, which is often related to sciatica.
- Physiotherapy for Nerve Pain Explains how physiotherapy can help with various nerve pain conditions, including sciatica.
- Exercise for Back Pain Offers exercise tips specifically aimed at reducing back pain and sciatica.
- Posture and Sciatica Discusses the relationship between posture and sciatica, with tips for improvement.
- Sciatica: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments Explains the symptoms, causes, and treatments of sciatica, offering comprehensive insights.
- Sciatica: Diagnosis and Treatment Provides detailed information on the diagnosis and treatment options for sciatica.
- Sciatica: What You Need to Know Offers a thorough overview of sciatica, including symptoms, causes, and treatment approaches.