What is Achilles Tendinopathy?
Achilles Tendinopathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Achilles tendinopathy, a common condition among athletes and active individuals, affects the Achilles tendon. This tendon, located at the back of your ankle, connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. When it becomes irritated or inflamed, it can cause significant pain and discomfort, impacting your ability to move freely.
What is Achilles Tendinopathy?
Achilles tendinopathy, often mistaken for Achilles tendonitis, is a chronic condition characterised by the degeneration of the Achilles tendon. Unlike tendonitis, which is an acute inflammation, tendinopathy involves the breakdown of the tendon’s collagen. This condition can be debilitating, leading to reduced performance and prolonged recovery times.
Differentiating Tendinopathy from Enthesopathy
While Achilles tendinopathy generally arises from repetitive strain, enthesopathy specifically involves the entheses, where tendons or ligaments attach to bone, and is characterised by inflammation, degeneration, or damage at these attachment points.
Read more: Achilles tendinopathy vs enthesopathy
Causes of Achilles Tendinopathy
Several factors contribute to the development of Achilles tendinopathy, including:
- Overuse: Repetitive strain from activities like running or jumping can lead to microtears in the tendon.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes that lack proper support can increase the risk.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly increasing the intensity or duration of physical activity can stress the tendon.
- Biomechanical Issues: Abnormal foot mechanics, such as flat feet or high arches, can place extra stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Age and Gender: Middle-aged men are particularly prone to developing this condition.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendinopathy
The symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy can vary but often include:
- Pain and Stiffness: Pain along the tendon, especially in the morning or after periods of rest, is common.
- Swelling: Swelling around the tendon or at the back of the heel.
- Thickening of the Tendon: The tendon may feel thicker or have nodules.
- Reduced Strength and Function: Difficulty in performing activities that involve the calf muscles, such as standing on tiptoe.
Diagnosis of Achilles Tendinopathy
A thorough assessment by a physiotherapist can diagnose Achilles tendinopathy. This typically involves:
- Medical History: Discussing your symptoms, activity levels, and any previous injuries.
- Physical Examination: Checking for pain, swelling, and tenderness along the tendon.
- Imaging: Ultrasound or MRI scans may be used to assess the extent of tendon damage.

Treatment and Rehabilitation of Achilles Tendinopathy
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for Achilles tendinopathy usually involves a combination of strategies:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing activities that aggravate the condition is crucial.
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can design an exercise program to strengthen the calf muscles and improve tendon resilience. Eccentric exercises, in particular, are beneficial.
- Orthotics and Footwear: Using shoe inserts or wearing supportive shoes can help correct biomechanical issues.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Shockwave Therapy: This non-invasive treatment can stimulate tendon healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the tendon.
Modern Approaches to Treatment
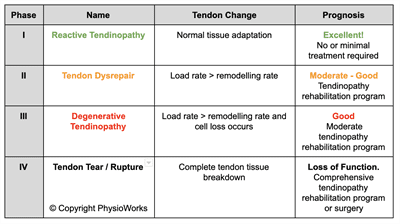
Recent research has led to significant advancements in treating Achilles tendinopathy. A tailored treatment plan, based on the specific phase of your injury, is crucial. This may involve specific exercises, managing activity loads, and monitoring progress through pain provocation tests and functional assessments.
Exercise’s Role in Recovery
Exercise, particularly isometric exercises, plays a crucial role in managing tendinopathy, providing pain relief, and aiding recovery. Progression in treatment is carefully monitored, with a focus on gradually increasing exercise loads to stimulate tendon growth while avoiding overloading.
Eccentric strengthening exercises are also recommended but should be introduced gradually to avoid aggravating the condition.
Importance of Load Management
Effectively managing your activity load is vital for successful recovery. Your physiotherapist will guide you in adjusting your exercise program based on your symptoms and response to activity. This includes modifying activities to prevent exacerbation of symptoms and ensuring recovery.
Avoiding Certain Exercises
Avoid exercises that exacerbate Achilles tendon pain, such as running uphill or performing deep squats, unless advised by your physiotherapist.
Complementary Therapies
Massage, foam rollers, and stretches can help release tension in associated muscle groups.
Addressing Adjacent Joints and Biomechanics
Biomechanical issues in the lower limb can increase the risk of Achilles tendinopathy. Your physiotherapist will assess and address any deficiencies in ankle dorsiflexion, squat alignment, and gluteal control, among other factors.
Exploring Novel Therapies
Emerging therapies, such as injections of sclerosing agents or platelet-derived growth factors, show promise but are still experimental. Consult your physiotherapist or sports doctor for advice on these treatments.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Healing Timeline
The healing timeline varies based on the tendinopathy phase, ranging from days to months. Early and appropriate management is key to quick recovery.
Preventing Achilles Tendon Rupture
A complete rupture of the Achilles tendon, though rare, is a severe complication. Early intervention and preventive measures are crucial to avoid this outcome.
Recent Research and Advances
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections in promoting tendon healing. PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s platelets into the affected area, potentially speeding up the recovery process.
What to Do?
If you suspect you have Achilles tendinopathy, seeking professional advice from your physiotherapist is essential. They can provide a tailored treatment plan to help you recover and prevent further injury.
Conclusion
Achilles tendinopathy can significantly impact your mobility and quality of life. Early intervention, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle modifications can effectively manage the condition and facilitate a return to regular activities.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateAchilles Tendinopathy FAQs
- What is Achilles tendinopathy? Achilles tendinopathy is a chronic condition involving the degeneration of the Achilles tendon, causing pain and stiffness.
- What causes Achilles tendinopathy? Overuse, improper footwear, sudden increases in activity, biomechanical issues, and age are common causes of Achilles tendinopathy.
- How is Achilles tendinopathy diagnosed? A physiotherapist, Orthopaedic surgeon or sports doctor will assess your medical history, perform a physical examination, and may use imaging like ultrasound or MRI to diagnose Achilles tendinopathy.
- What are the symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy? Symptoms include pain and stiffness along the tendon, swelling, thickening of the tendon, and reduced strength and function.
- How can physiotherapy help with Achilles tendinopathy? Physiotherapy involves exercises to strengthen the calf muscles, improve tendon resilience, and may include treatments like shockwave therapy.
- Are there any new treatments for Achilles tendinopathy? Recent advances include platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, which can promote tendon healing and speed up recovery.
Related Articles
- Achilles Enthesopathy: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment: Readers can explore the specific condition of Achilles Enthesopathy, which is a related pathology affecting the Achilles tendon area.
- How Do You Treat Achilles Tendinopathy?: This article delves into various treatment options for Achilles Tendinopathy, providing valuable insights for readers seeking recovery methods.
- Achilles Rupture: Causes, Treatment & Management Options: This resource discusses the severe complication of an Achilles rupture, which is a crucial aspect of understanding the full spectrum of Achilles tendon issues.
- Tendinopathy: Causes, Symptoms, And Effective Treatments: An informative piece on general tendinopathy, giving readers broader context on tendon issues, including the Achilles tendon.
- Heel, Foot, And Ankle Pain: Your FAQs Answered: This article answers frequently asked questions about foot and ankle pain, which can be associated with Achilles tendinopathy.
- Common Tendinopathies: An Overview Of Tendon Injuries: Provides a broader perspective on various tendinopathies, enriching the reader’s understanding of tendon injuries including the Achilles tendon.
- Heel Pain: Since Achilles tendinopathy can cause heel pain, this article would be useful for readers experiencing similar symptoms.
- Tibialis Posterior Tendinopathy: This article covers another tendinopathy that affects the lower limb, providing a comparative perspective.