Back Pain: Causes, Remedies, and Prevention
What is Back Pain?
Back pain, especially in the lower lumbar region, affects many Australians throughout their lives. Injuries or strains to the muscles, ligaments, or joints of the lower spine typically cause this pain. These injuries might result from sudden actions like lifting heavy items or from prolonged poor habits such as slouching. Seeking early diagnosis and treatment from a physiotherapist can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent future episodes. Moreover, adopting preventative steps, including maintaining good posture and doing specific exercises, can decrease the risk of experiencing back pain.
What Triggers Back Pain?
Musculoskeletal problems such as muscle strains, ligament sprains, disc bulging, and joint dysfunction frequently result in lumbar pain. Traumatic incidents like lifting heavy loads or prolonged stress injuries can also lead to pain. Early diagnosis and treatment from a physiotherapist can help in prevention and recovery. Additionally, adopting measures to fend off future episodes is crucial.

Frequent Back Pain Causes
Muscle & Ligament Strains
Overworking or tiring the muscles in the lower back, especially from heavy lifting or poor posture, leads to back pain. Weak back muscles might also reduce joint stabilisation, causing further issues. Physiotherapists recommend proper posture and exercises to relieve pain and prevent future muscle-related back pain.
Ligaments, which connect bones and restrict movement, can tear if stretched excessively, causing pain and swelling. Common reasons for such injuries include awkward lifting, sporting mishaps, or car accidents. Physiotherapy effectively treats ligament injuries, speeding up healing and relieving painful symptoms.
Read more: Back Muscle Pain
Bulging Discs
Damage to the intervertebral discs in the spine can cause a bulging disc injury. When a disc bulges, it can press on spinal nerves, resulting in back pain, muscle spasms, or even numbness. Repetitive stress, poor posture, or trauma can cause a bulging disc. A physiotherapist can provide guidance on managing this condition.
Read more: Bulging Discs
Degenerative Disc Disease
As we age, the intervertebral discs in our spine can degenerate, leading to pain. This condition, known as degenerative disc disease, can result in chronic discomfort and reduced mobility. A physiotherapist can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Read more: Degenerative Disc Disease
Bone Injuries
High trauma or low bone density conditions like osteoporosis can lead to spine fractures. Maintaining bone health through diet, exercise, and medical guidance is essential.
Read more: Osteoporosis
Poor Posture
Slouching or maintaining an improper posture can strain the spine, leading to back pain. Physiotherapists can provide advice on posture correction and exercises to strengthen the back muscles.
Read more: Back Posture Explained
How Can We Prevent Back Injury?
Engaging in regular exercise and keeping the spine and core muscles strong and flexible can lower the risk of injury. Adopting proper posture and using safe lifting methods also prove beneficial. For tailored advice on posture and movement, consider consulting a physiotherapist.
Back Pain Treatment
When addressing lower spine injuries, treatment goals set by a physiotherapist might vary based on the specific diagnosis. However, common objectives include reducing pain, enhancing mobility, strengthening spine-supporting muscles, educating on proper posture, and addressing root causes of the symptoms.
Treatment Phases
- Pain Relief & Protection: The primary objective is managing acute symptoms. Physiotherapists often use tools like ice therapy, electrotherapy, acupuncture, supportive taping, and massage. Some people also find non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen helpful.
- Restoring Normal ROM & Strength: As pain subsides, physiotherapists work on restoring spine motion, muscle tension, strength, balance, and proper gait. They might also introduce core stability exercises to enhance control and stability of the lower spine and pelvis.
- Full Function Restoration: Depending on personal goals, whether it’s a casual walk or an intense sport, physiotherapists tailor the rehabilitation to ensure a safe return to desired activities.
- Preventing a Recurrence: To avoid recurrent back pain, it’s crucial to continue with a version of the exercises introduced during treatment.
Other Treatment Options
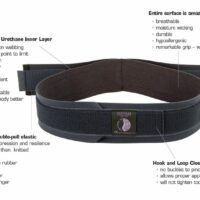
Physiotherapists might suggest other treatments like manual therapy, exercises, ice, ultrasound, TENS, and posture education. Other options include back braces, dry needling, acupuncture, massage, TENS machines, posture supports, and weight loss strategies for those who might benefit.
Expected Results from Back Pain Treatment
Recovery from back injury generally spans 4 to 6 weeks. However, individual experiences may vary. Adhering to the treatment plan set by your physiotherapist remains crucial for a successful recovery.
New Research on Back Pain
Recent studies have provided insights into effective treatments for back pain. A systematic review by Wong et al. (2023) highlighted the benefits of exercise therapy for chronic back pain, emphasising core strengthening and flexibility exercises. Another study explored the efficacy of manual therapy combined with exercise, showing significant improvements in pain relief and functional mobility.

Conclusion
Back pain, a common ailment experienced by many Australians, often stems from various causes, from muscle strains to poor posture. While it can be debilitating, understanding its origins and seeking timely intervention from professionals, especially physiotherapists, can make a world of difference. Adopting preventive measures and maintaining an active lifestyle, coupled with good posture, can significantly reduce the risk of developing back pain. Remember, your back supports you in every endeavour; give it the care and attention it rightly deserves. If you ever experience persistent back issues, seeking professional advice early can set you on a path to a pain-free life.
What to Do?
If you experience persistent back pain, consult a physiotherapist to get a tailored treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and help you return to your normal activities.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateBack Pain FAQs
1. What are the main causes of back pain?
Back pain can result from various factors such as muscle strains, ligament sprains, disc bulging, degenerative disc disease, and poor posture. Each cause requires specific treatment and prevention strategies. For more detailed information: Back Pain Causes Discussed.
2. How can I prevent back pain?
Preventing back pain involves regular exercise, maintaining good posture, and using safe lifting techniques. Strengthening the core muscles and keeping the spine flexible are crucial steps. Consult a physiotherapist for personalised advice. Read more: Back Pain Prevention.
3. What treatments are available for back pain?
Treatments for back pain include manual therapy, exercises, ice therapy, ultrasound, TENS, and posture education. Physiotherapists tailor treatment plans based on individual needs. Learn more about: Back Pain Treatment Options.
4. How effective is physiotherapy for back pain?
Physiotherapy is highly effective in treating back pain by addressing the root cause, reducing pain, and restoring normal function. It includes various techniques such as manual therapy and specific exercises. Read more: Back Pain Physiotherapy Benefits.
5. How long does it take to recover from back pain?
Recovery from back pain generally takes 4 to 6 weeks, but it varies depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. Following a physiotherapist’s treatment plan is essential for a successful recovery. Find out more about back pain recovery times.
6. What should I do if my back pain persists?
If your back pain persists, consult a physiotherapist for a comprehensive assessment and tailored treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening. Read more about when to seek help for persistent or severe back pain.
Follow Us for Free Tips
For more tips on managing back pain and improving your life, follow us on social media. Stay updated with the latest advice and support from our physiotherapists.
Related Articles
- Back Pain Physiotherapy: Your Guide To What To Expect – This article provides a comprehensive guide to what one can expect during physiotherapy for back pain.
- Sudden Back Pain Explained: Causes & Physiotherapy Solutions – It discusses into the causes of sudden back pain and offers physiotherapy solutions.
- Lower Back Pain – Understanding & Managing – This guide explores different factors contributing to lower back pain and offers management tips.
- Effective Back Exercises And Core Strength: Physio Insights – Focuses on back exercises and core strength as key elements in managing lower back pain.
- Core Stability Training For Effective Low Back Pain Relief – Highlights the importance of core stability training in relieving low back pain.
- What Causes Back Pain For No Reason? – Addresses unexplained back pain and how physiotherapy can assist in managing it.
- Core Stability: A Physiotherapist’s Guide For Spinal Health – Provides a physiotherapist’s perspective on core stability for spinal health.
- Back Posture Correction – Discusses how posture correction can effectively manage back pain and injury.
- Spinal Stenosis – Offers insights into spinal stenosis and its connection to lower back pain.
- Posture Exercises – Highlights the importance of posture exercises in preventing and alleviating back pain-related issues.
- Back Pain – Symptoms and Causes
- Back pain — an overview