Morton's Neuroma
Article by Alex Clarke
Morton’s Neuroma
What is Morton’s Neuroma?
A Morton’s Neuroma is incorrectly termed, with the name suggesting it is a tumour or growth. Rather than a true neuroma, it is perineural fibrosis, which means that over time the sheath surrounding the nerve becomes irritated, inflamed, and forms a thickened scar tissue.
Morton’s Neuroma Symptoms
It usually occurs between the 3rd and 4th toes (about 65% of cases). It is less commonly found in the 2nd web space and rarely in the 1st or 4th web spaces. You can also experience pins and needles or numbness due to the nerve being affected. The condition tends to occur predominantly in middle-aged females.
What Causes Morton’s Neuroma?
A Morton’s Neuroma is a result of complex biomechanical changes that occur in your feet. There are many theories about the exact cause of the scarring and thickening, but it boils down to a tissue overload. The body lays down scar tissue to try to protect the overloaded structure.
Tight-fitting shoes may exacerbate a Morton’s Neuroma. Shoes such as high heels and shoes with tight toe boxes (e.g. women’s fashion shoes and cowboy boots) are particularly damaging to the toes. These shoes have a sloping footbed and a narrow toe box. The slope causes the front of the foot to bear your weight. The angle of the toe box then squeezes your toes together.
Footwear is not the only cause of Morton’s Neuroma. Injuries to the foot can also factor in developing the condition by changing your foot biomechanics. Poor foot arch control that leads to flat feet or foot overpronation may make you susceptible to a neuroma. This predisposition is due to biomechanical reasons.
For specific advice regarding your Morton’s Neuroma, please consult your foot physiotherapist, podiatrist or doctor.
Morton’s Neuroma Treatment
PHASE I – Pain Relief. Minimise Swelling & Injury Protection
Pain is the main reason that you seek treatment for a neuroma. Analgesics may help. Ease your inflammation via ice therapy and techniques or exercises that unload the inflammed structures. Anti-inflammatory medications may help.
Your physiotherapist will use various treatment tools to reduce your pain and inflammation. These include ice, electrotherapy, acupuncture, unloading taping techniques, soft tissue massage and orthotics to offload the irritated nerve.
One of the most significant factors in relieving pain may be changing or modifying your footwear. An adjustment may mean adding felt, foam or gel products to your shoe to help offload the area or avoiding tight-fitting heels or boots.
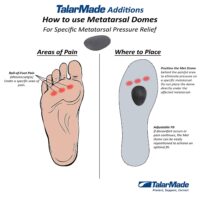
Metatarsal domes are often very useful.
Sometimes a corticosteroid injection is required to help settle the inflammation surrounding the nerve. It would be best if you experienced good pain relief with a steroid injection. However, there are some risks that you should discuss with your physio or doctor.
PHASE II – Restoring Normal ROM & Posture
As your pain and inflammation settle, your physiotherapist will focus on restoring your standard toe and foot joint range of motion and muscle length.
Treatment may include joint mobilisation and alignment techniques, massage, muscle and joint stretches, taping, or orthotics. Your physiotherapist is highly skilled in the methods that will work best for you.
PHASE III – Restore Normal Muscle Control & Strength
Your foot posture muscles are vital to correct the biomechanics that led to the overload injury. Your physiotherapist will assess your foot posture muscles and prescribe the best exercises specific to your needs.
PhysioWorks has developed a “Foot Posture Correction Program” to help you regain your healthy foot posture. Please ask your physio for their advice.
PHASE IV – Restoring Full Function
This stage of your rehabilitation aims at returning you to your desired activities. Everyone has different demands for their feet that will determine what specific treatment goals you need to achieve. For some, it is merely to walk around the block. Others may wish to run a marathon or return to a labour-intensive activity. Your physiotherapist will tailor your rehabilitation to help you achieve your own functional goals.
PHASE V – Preventing a Recurrence
A Morton’s Neuroma may recur with repeated overload. The main reason is biomechanical. In addition to your muscle control, your physiotherapist will assess your foot biomechanics and may recommend a temporary off-the-shelf orthotic or refer you to a podiatrist for custom-made orthotics. You should avoid wearing high-heeled shoes with tight or angular toe boxes. Your physiotherapist will guide you.
Morton’s Neuroma Surgery
Consider surgery when the non-operative treatment cannot relieve your symptoms, particularly if you have had pain for more than six months. 80% of patients who require surgery report good results, with 71% of people becoming pain-free.
Please consult your foot physiotherapist, podiatrist or doctor for individualised advice.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateCommon Foot Pain Causes


Various factors, ranging from injuries and tendon problems to degenerative conditions and systemic diseases, can cause foot pain. Some common causes of foot pain include foot injuries, plantar fasciitis, bunions, metatarsalgia, Morton's neuroma, tendon injuries, bone injuries, degenerative conditions like arthritis, biomechanical issues, nerve-related sources such as tarsal tunnel syndrome, and muscle injuries.
Certain systemic conditions like fibromyalgia, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis can also contribute to foot pain. This comprehensive list covers a wide range of foot pain causes, encompassing different areas of the foot and various underlying conditions.
Foot Injuries
Tendon Injuries
- Achilles Tendon Rupture
- Achilles Tendinopathy
- FHL Tendinopathy
- Peroneal Tendinopathy
- Tibialis Posterior Tendinopathy
Bone Injuries
- Ankle Fracture (Broken Ankle)
- Stress Fracture
- Stress Fracture Feet
- Severs Disease
- Osteochondritis Dissecans
- Heel Spur
- Shin Splints
Traumatic Ankle Ligament Injuries
Degenerative Conditions
Soft Tissue Inflammation
Biomechanical Conditions
Nerve-Related Sources
Muscle Injuries
Systemic Conditions
Soft Tissue Inflammation
Other Useful Information
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateFoot, Ankle & Heel Pain FAQs
Introduction
Welcome to PhysioWorks' comprehensive FAQ page on Foot, Ankle, and Heel Pain. Our expert physiotherapists are here to guide you in managing and overcoming discomfort. We’ve organised the FAQs into categories, each with a brief overview and links to in-depth articles, making navigation and understanding easier for you.


Foot Pain
Step into the various causes of foot pain and learn effective ways to relieve discomfort. Understand the impact of activities like barefoot running.
Ankle Injuries
Explore common ankle injuries and how to address them. From sprains to ligament damage, find out the best practices for care and prevention.
Heel Pain
Uncover the reasons behind heel pain and the effective treatments available. This section is particularly useful for understanding conditions like plantar fasciitis and heel spurs.
Achilles Pain
Find out how to manage and treat Achilles tendinopathy, a common concern for athletes and active individuals.
Shin Pain
Learn about shin splints, their causes, and how to alleviate this common issue, especially among runners.
Youth Injuries
Gain insights into youth leg injuries, including growing pains and heel issues in children.
Balance & Proprioception
Enhance your balance and proprioception with our professional advice and exercises.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateRelated Articles
- Sprained Ankle Treatment & Recovery Guide: Offers detailed advice on how to manage sprained ankles, including immediate recovery steps and physiotherapy treatments.
- Ankle Pain: Effective Management And Treatment Options: Discusses various conditions leading to ankle pain and outlines effective treatment strategies, highlighting the role of physiotherapy in pain reduction and mobility improvement.
- Plantar Fasciitis: Provides an overview of plantar fasciitis, including common causes, treatment options, and related conditions like peroneal tendinopathy and Achilles tendinopathy.
- Achilles Tendinopathy: Focuses on the causes of Achilles tendinopathy, its impact on heel pain, and a range of treatment and prevention strategies.
- Ankle Strapping: Complete Guide To Injury Prevention: Explains the benefits of ankle strapping as a preventative measure against injuries, with a focus on techniques and materials.
- Heel Pain: Explores various causes of heel pain, including tendon injuries, foot injuries, bone injuries, and systemic conditions, alongside recommended treatments.