Article by John Miller
What's the Best Treatment for SIJ & Buttock Pain?
Understanding SIJ and Buttock Pain
Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) and buttock pain can disrupt your daily life. A physiotherapist tailors treatment to your specific diagnosis, focusing on relieving pain, restoring function, and preventing future issues.


Phase I: Relieving SIJ Pain and Protecting the Joint
To start, pain relief is crucial. Acute SIJ dysfunction may require pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications. However, these don't address the root cause. Your physiotherapist, with a thorough understanding of SIJ biomechanics and muscle control, will evaluate chronic cases. Managing sacroiliac pain, the primary symptom prompting treatment, is essential. Natural pain relief can be achieved using ice or heat packs on the SIJ.
Next, focus on reducing inflammation. Ice therapy, specific exercises, and techniques to unload inflamed structures are effective. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, like ibuprofen, may be recommended. In some cases, blood tests can diagnose conditions like seronegative arthritis (eg Ankylosing Spondylitis), which can predispose you to sacroiliitis. Addressing prolonged morning stiffness, particularly in conditions like Ankylosing Spondylitis, is also important.
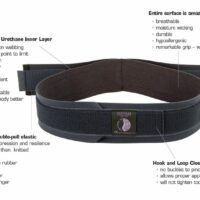
For SIJ instability, passive support, such as supportive taping or a sacroiliac joint stabilisation belt, can be helpful. However, a tailored exercise program is generally more effective.
Phase II: Restoring Normal Movement and Strength
As pain and inflammation subside, the focus shifts to restoring pelvic joint alignment and normal muscle control. Your physiotherapist may introduce a core stability program targeting lower abdominal muscles to stabilise your lower back and pelvis. Additionally, strengthening deep gluteal muscles, sometimes called your hip core muscles, is crucial. Your physiotherapist will assess your muscle recruitment pattern to determine the most suitable exercises.
Phase III: Regaining Full Function
This phase aims to return to normal pelvic alignment and maintain sacroiliac joint range of motion during demanding activities. Improving muscle power, balance, and gait is essential. Your physiotherapist tailors the treatment to your specific needs, whether you aim to walk comfortably or run a marathon.
Phase IV: Preventing Future Issues
Preventing recurrent sacroiliac joint dysfunction involves committing to a thorough muscle control program. Chronic SIJ issues often stem from muscle weakness. Your physiotherapist will guide you in identifying the best exercises to continue regularly.
Beyond muscle control, evaluating SIJ, spine, hip, and lower limb biomechanics is crucial. Addressing deficiencies helps prevent SIJ pain and dysfunction. Learning self-management techniques and receiving professional guidance from your physiotherapist will ensure long-term stability and function.
Conclusion
Effective SIJ and buttock pain treatment requires a comprehensive approach. Relief, restoration, and prevention are the key steps. By following a structured plan and seeking professional advice, you can manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
What to Do?
For personalised advice and treatment, please consult your physiotherapist. They will create a tailored plan to address your SIJ and buttock pain, ensuring you regain function and prevent future issues.
Read more: Sacroiliac Joint Pain
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateSIJ FAQs
- What causes SIJ pain?
- SIJ pain can result from injury, arthritis, pregnancy, or prolonged sitting.
- How is SIJ pain diagnosed?
- Diagnosis involves physical exams, imaging tests, and sometimes diagnostic injections.
- What are the symptoms of SIJ pain?
- Symptoms include lower back pain, buttock pain, and discomfort when sitting or standing.
- Can exercise help with SIJ pain?
- Yes, specific exercises can strengthen muscles and stabilise the SIJ.
- Is SIJ pain permanent?
- With proper treatment, SIJ pain can often be managed and reduced.
- When should I see a physiotherapist for SIJ pain?
- If you experience persistent pain or discomfort in your SIJ, consult a physiotherapist for evaluation and treatment.
Related Articles
- Sacroiliac Joint Pain
- Learn about the causes and treatments for sacroiliac joint pain.
- Lower Back Pain
- Discover effective strategies to manage and treat lower back pain.
- Hip Pain
- Understand the various causes of hip pain and how to treat them.
- Arthritis Management
- Explore comprehensive approaches to managing arthritis pain.
- Core Stability Exercises
- Find out how core stability exercises can benefit your overall health.
- Sports Injury Prevention
- Learn tips and techniques to prevent sports injuries.
- Gait Analysis
- Discover how gait analysis can help improve your walking pattern.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Get detailed information on managing Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Muscle Pain Relief
- Explore effective methods for relieving muscle pain.
- SI Joint Dysfunction: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
- Understand the causes, symptoms, and treatments for SI joint dysfunction.
- Managing SI Joint Pain
- Discover how to manage SI joint pain effectively.
- Exercises for SI Joint Pain Relief
- Learn specific exercises that can help relieve SI joint pain.