Squash Injuries
Article by John Miller

Common Squash Injuries
Squash players often suffer from injuries as the game requires repetitive use of their spine, legs, and dominant arm at high speeds. The game involves using a racquet and a ball, and injuries can occur anywhere from the shoulder, elbow, and wrist to the hip, knee, ankle, and spine. Additionally, there is a risk of head and eye injuries from the ball or racquet, and collisions with the walls can also cause injuries.
Most squash injuries occur due to acute incidents rather than overuse. However, squash players commonly experience lateral epicondylalgia, an overuse injury affecting the upper limb. Squash players often refer to lateral epicondylalgia, also known as tennis elbow, as squash elbow due to its frequent occurrence in the sport.
Overuse injuries affecting the wrist and knee are also common in squash. De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a common wrist injury caused by the inflammation of the tendons below the thumb. Squash players can also suffer from patellar tendinopathy, an overuse injury affecting the knee tendons due to the constant stress of running and change of direction in sports.
Squash players are susceptible to various acute injuries, such as head and facial injuries, especially to the eyes. Strains often affect the shoulder, wrist, and elbow. Eye injuries can range from a scratched cornea (front surface of the eye), retinal detachment, and globe rupture to hyphema (blood collection in the front of the eye).
Due to squash’s fast and agile nature, players commonly experience sprained ankles, calf muscle tears, back muscle strains, knee ligament sprains, knee meniscal tears, and even Achilles tendon ruptures.
What Causes Injuries in Squash?
Various factors influence the risk of injury in squash due to the sport’s unpredictable nature.
Repetitive arm movements, especially at high velocities required in squash, cause overuse injuries such as lateral epicondylalgia in the elbow and de Quervain’s tenosynovitis in the thumb.
Frequent use of the gripping muscles in the forearm, particularly those that extend or bend the wrist backward, aggravates the elbow injury. Backhand shots can worsen inflammation in this area due to the immense force required by wrist extensors.
Gripping and turning the wrist over can worsen injuries in the wrist/thumb, which can affect a player’s ability to perform powerful shots.
Eye/facial injuries usually occur due to a collision with the ball or racquet. Such injuries can be severe and require immediate medical attention to prevent vision loss. Wearing safety eyewear is recommended.
Impact due to diving or collisions with the wall can cause shoulder injuries, especially acromioclavicular joint sprains. Such injuries disrupt the ligaments that connect the shoulder to the collarbone. Falls or collisions with hard surfaces can cause wrist, hand, and elbow injuries.
Lower limb injuries are prevalent due to the rapid change of direction required in squash, including sprinting, pivoting, sudden stopping, and jarring. Joints and muscles under high strain lead to injury when the load surpasses the healing recovery rate.
If you sustain an injury while playing squash, don’t hesitate to contact your physiotherapy team for accurate diagnosis and assistance getting back on the court as quickly as possible.
Risk Factors for Squash Injuries
The following factors increase the risk of injuries in squash:
- Being 40 years of age or older
- Having limited experience or poor technique
- Having a low level of fitness, strength, and endurance
- A prior injury, especially if not appropriately rehabilitated, significantly increases the risk of further injury.
- Participating in squash frequently and at a high level
- Not wearing protective eyewear
- Using improper equipment or footwear
- Experiencing fatigue and tissue overloading due to overuse or inadequate rest periods.
If you have any of these risk factors, taking appropriate precautions and seeking advice from a qualified professional to prevent or manage injuries is essential.
How Can Squash Injuries Be Prevented?
To prevent squash injuries, take the following measures:
- Wear protective gear such as glasses to prevent eye injuries.
- Perform strength, coordination and balance exercises to prevent soft tissue, bone, or joint injuries.
- Consult with your physiotherapist for guidance specific to your body.
- Warm up before exercise and cool down after playing to decrease the risk of muscle strains.
- Perform change of direction and landing exercises to prevent lower limb joint injuries.
- Perform shoulder and arm exercises to prevent injuries in these areas.
- Recover well with stretching and foam rolling to decrease post-activity muscle tightness/stiffness.
- Consult your physiotherapist for tendinopathy programs to rehabilitate you from injury and prevent tendon injuries successfully.
- Speak to your physiotherapist to tailor an exercise program specifically for you.
- Rehabilitate appropriately in the event of injury to minimise the risk of re-injury or compensatory injury when returning to squash.
Your PhysioWorks physiotherapy team can provide you with an accurate diagnosis and assistance in returning you to the court as quickly and safely as possible.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateArticle by Zoe Russell
Sports Physiotherapy FAQs
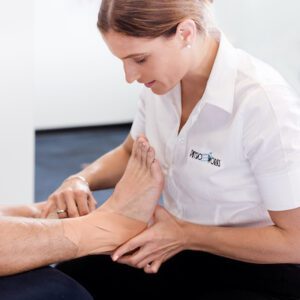

Sports Physiotherapy is the specialised branch of physiotherapy which deals with injuries and issues related to spokespeople. Practitioners with additional formal training within Australia are Sports & Exercise Physiotherapists.
What is Sports Physiotherapy?
Sports injuries do differ from common everyday injuries. Athletes usually require high-level performance and demands placed upon their bodies, which stresses their muscles, joints and bones to the limit. Sports physiotherapists help athletes recover from sporting injuries and provide education and resources to prevent problems. Each sports physiotherapist usually has sport-specific knowledge that addresses acute, chronic and overuse injuries. Their services are generally available to sportsmen and women of all ages engaged in sports at any level of competition.
Members of Sports Physiotherapy Australia (SPA) have experience and knowledge of the latest evidence-based practice, professional assessment and diagnosis of sports injuries, and effective hands-on management techniques and exercise protocols to assist recovery and prevent future damage. SPA members have access to the most recent advances in sports physiotherapy. You'll be pleased to know that most PhysioWorks physiotherapists and massage therapists are particularly interested in sports injury management.
General Sports Physio FAQs
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Acute Sports Injury Clinics
- Sports Physiotherapy Treatment
- Youth Sports Injuries
Injury Management
- Sports Injury? What to do? When?
- When Can You Back to Sport?
- Sports-Related Injuries
- Knee Sports Injuries
- Sports Health Conditions
Sports Massage
Sports Insurance
Related Articles
- Sports Injury Management: This article provides a comprehensive look at how sports injuries are managed, including prevention strategies and treatment options.
- Soft Tissue Injury Healing: Readers can learn about the healing process for soft tissue injuries, including practical advice for each phase of recovery.
- Prehabilitation: Key to Injury-Free Sports Performance: Offers insights into how athletes can prevent injuries before they occur, focusing on strengthening and conditioning practices.
- Athletics Injuries - Comprehensive Physio Guide: A detailed guide on common injuries in athletics and how to treat and prevent them, making it a valuable resource for athletes of all levels.
- Acute Sports Injury Clinic: Highlights the services offered by sports injury clinics, including fast-track assessments and treatments for acute sports injuries.
- Effective Management of Kids Sports Injuries: This guide focuses on the unique aspects of managing sports injuries in children, offering parents and coaches valuable advice on care and prevention.
More Information
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateCommon Muscle Injuries
A Physiotherapist's Guide
Introduction
Muscle injuries, presenting as muscle strain, pain or myalgia, are prevalent health issues affecting a wide range of individuals. This detailed guide, from a physiotherapist's perspective, delves into various muscle injuries, elaborating on their management, prevention, and the importance of professional advice. Explore the linked articles for an in-depth understanding of muscle injuries and their effective treatment.
Neck & Back Muscle Injuries: Causes and Solutions
- Back Muscle Pain: This pain often results from prolonged poor posture or physical overuse. Key to relief is engaging in exercises that strengthen the core muscles and improve posture, thereby alleviating the strain on the back.
- Neck Sprain: Caused by sudden, awkward movements, a neck sprain can benefit from a combination of gentle stretches and targeted strengthening exercises to restore flexibility and strength.
- Text Neck: A modern ailment resulting from extended mobile device use, text neck can lead to chronic pain. Regular breaks, posture-awareness, and neck-strengthening exercises are essential for prevention.
- Whiplash: Commonly occurring in car accidents, whiplash requires a careful approach including neck stabilisation exercises and controlled movement to encourage healing and prevent further injury.
Lower Limb Muscle Injuries: Understanding and Treating
- Hamstring Strain: Particularly common among athletes, particularly runners, this strain demands rest initially, followed by a carefully structured rehabilitation program focusing on gradual strength building and flexibility.
- Thigh Strain: Often seen in sports involving sprinting and jumping, thigh strains need a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) in the initial stages, followed by carefully planned strengthening exercises.
- Groin Strain: This injury requires a nuanced approach, including sufficient rest and targeted exercises, to ensure a safe and effective recovery.
- Calf Muscle Tear: Key to recovery is a balance of rest, gentle stretching exercises, and a gradual return to full activity, ensuring the muscle heals correctly and strength is regained.
Upper Limb Muscle Injuries: Prevention and Care
- Golfer's Elbow and Tennis Elbow: Both these conditions involve inflammation of the tendons and require a rest period, followed by ice therapy and specific exercises tailored to strengthen the affected muscles.
- Corked Thigh: Resulting from direct impacts, these injuries demand immediate application of ice and a controlled, gradual exercise regime for recovery.
- DOMS, Fatigue-Related Cramps & Myalgia: Adequate rest, good hydration, and gentle stretching are crucial in alleviating these conditions.
- RSI: Regular stretching, ergonomic workplace adjustments, and taking breaks are key preventive measures for repetitive strain injury.
Systemic Causes of Muscle Pain: A Holistic View
- Fibromyalgia: This complex condition demands a holistic treatment approach, including exercise routines, stress management techniques, and sometimes medication.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Effective management combines medication, gentle exercise, and regular physiotherapy sessions.
Prevention and Management Strategies
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain muscle strength and flexibility, reducing the risk of muscle injuries.
- Posture Improvement: Good posture, both in motion and at rest, is crucial for preventing muscle strain.
- Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Adequate warm-up before and cool-down after physical activity is vital in preventing muscle strains and injuries.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Making ergonomic adjustments at work and during daily activities can significantly reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries and other muscle-related issues.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Keeping a healthy weight reduces the strain on muscles, particularly in weight-bearing joints.
What to Do? Seeking Professional Advice
Consult a physiotherapist or doctor for personalised advice and treatment plans. Remember, early intervention can significantly improve recovery outcomes and prevent chronic problems.
Conclusion
While muscle injuries are common, effective management and prevention are achievable with the right approach and knowledge. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and various treatments available empowers individuals to take proactive steps in their recovery and prevention. For the most tailored and effective treatment, always seek the guidance of a professional physiotherapist.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateCommon Ligament Injuries


Ligament Injury
Ligament injuries frequently occur in various body parts, leading to pain and restricted movement. The most common sites include the knee, ankle, shoulder, wrist, hand, and spine.
Notably, knee injuries like ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL sprains are prevalent.
Shoulder injuries often involve the AC joint, while wrist and hand issues can include thumb and finger sprains.
Spinal ligament injuries, such as back and neck sprains, and whiplash, are also significant. Understanding these injuries helps in prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.
- Ankle Ligament Injuries
- Knee Ligament Injuries
- Shoulder Ligament Injuries
- Wrist & Hand Ligament Injuries
- Spinal Ligament Injuries
Ankle Ligament Injuries
Ankle injuries often result from sudden twists or rolls, leading to sprains and strains.
Knee Ligament Injuries
Knee ligament injuries are among the most common and can severely impact mobility and quality of life.
- ACL Injury
- PCL Injury
- MCL Sprain
- LCL Sprain
- Posterolateral Corner Injury
- Patella Dislocation
- Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprain
Shoulder Ligament Injuries
Shoulder ligament injuries can be debilitating, affecting a range of movements.
Wrist & Hand Ligament Injuries
Injuries in the wrist and hand are common, especially in sports and physical activities.
Spinal Ligament Injuries
Spinal ligament injuries can result from various causes, including posture issues and physical impacts.
Related Articles
- Ligament Tear - Common Ligament Injuries: Offers a comprehensive overview of ligament injuries across different body parts, including prevention, early detection, and effective treatment strategies.
- Knee Ligament Injury - A Physiotherapist's Guide & Tips: Provides insights into diagnosing knee pain, covering ligament issues among other concerns, and suggests pain relief methods through exercise and treatment.
- Common Ankle Ligament Injuries: A Physiotherapist's Guide: Discusses the treatment and prevention strategies for ankle ligament injuries, emphasising the importance of early intervention.
- Sprained Ankle Treatment & Recovery Guide: Offers detailed guidance on the recovery timelines for sprained ankles, highlighting the importance of restoring strength, motion, and function for a full recovery.
- Ankle Strapping: Complete Guide To Injury Prevention: Focuses on preventing ankle injuries through effective strapping techniques and discusses conditions like ankle arthritis and biomechanical issues.
- Sub-Acute Soft Tissue Injury: Explores the treatment and recovery process for various ligament injuries, including those affecting the knee, shoulder, wrist, hand, and spine.
- Sprained Thumb Treatment And Recovery Tips: Delivers practical tips for treating and recovering from a sprained thumb, along with general management strategies for wrist and hand pain.













































































