Soft Tissue Injury Care
Article by John Miller

Soft Tissue Injuries
What is a Soft Tissue Injury?
A soft tissue injury is any injury within your soft tissues, such as muscle, ligaments, tendons and fascia. In other words, non-bone related injuries.
Soft tissue injuries include:
- Muscle Strains
- Ligament Sprains
- Tendon Injuries, e.g. tendinopathy
- Other Soft Tissue Injuries (e.g. fat, myofascial tissue, joint capsules, skin and other connective tissue)
Seek Professional Advice
The best care is to seek prompt medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and specific care. However, in the interim, you can follow the following general guidelines.
In the first three days after injury, use the R.I.C.E. method:
- Rest (to avoid pain and further damage)
- Ice (20 to 30 minutes, each two to three hours)
- Compression (to support the injury and minimise swelling)
- Elevation (above your heart to assist in swelling reduction)
You will help your chances of a full recovery if you avoid the H.A.R.M. factors in the first 48 to 72 hours.
What are the HARM Factors?
Heat: Increases swelling and bleeding. Avoid heat packs, a hot bath and saunas.
Alcohol: Increases swelling and bleeding. Plus, it can delay healing.
Running or Exercise: Aggravates the injury, increasing pain, swelling and bleeding. Always check with a health professional before resuming sport or exercise.
Massage: Increases swelling and bleeding. Direct massage to the injured area may aggravate the damaged tissues and is normally best avoided for the first 48 to 72 hours. Indirect massage (away from the injury site) may be helpful. Please consult your health practitioner for the best advice for your injury.
What is Your Subsequent Treatment?
While the following advice is generic and may vary depending on your injury diagnosis, several treatment goals during the subacute phase, include:
Pain Relief
Is it important to ease and safely manage your pain? While natural products such as ice and over-the-counter medications may assist you, the advice of a health professional is the safest option for you to control your pain. Sometimes, using an electronic device such as a TENS machine may also assist your early pain relief.
Regain Full Movement
Once the initial trauma has settled, the primary aim of treatment is to regain your full joint, ligament and muscle range of motion. Your physiotherapist will identify abnormalities, provide hands-on treatment, and prescribe relevant exercises to regain normal movement.
Muscle Strengthening
It is crucial to support the muscles surrounding your injury via strengthening exercises. This muscle control is important to support during the early recovery phase, prevent re-injury, and return you to everyday function and sport. Your physiotherapist will prescribe and progress injury-specific exercises individualised to your needs.
Proprioceptive Retraining
An injury causes nerve pathway damage that affects your ability to control your joint position. The technical name for this is proprioception. Proprioception exercises have been shown in numerous research studies to prevent future injuries. Your physiotherapist is highly skilled in proprioceptive retraining. They will prescribe specific functional and sport-related proprioceptive exercises.
Heat or Ice
Heat can ease muscle soreness, increase soft tissue extensibility, and increase circulation. Ice has also been useful beyond 72 hours post-injury to reduce swelling due to excessive use and slow your nerve conduction rate to assist pain control. Please consult your physiotherapist if you would like advice regarding what is most suitable for you.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateArticle by Zoe Russell
Sports Physiotherapy FAQs
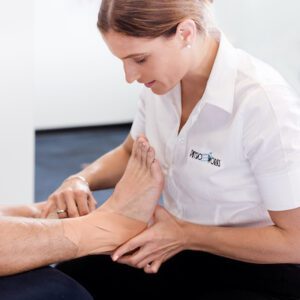

Sports Physiotherapy is the specialised branch of physiotherapy which deals with injuries and issues related to spokespeople. Practitioners with additional formal training within Australia are Sports & Exercise Physiotherapists.
What is Sports Physiotherapy?
Sports injuries do differ from common everyday injuries. Athletes usually require high-level performance and demands placed upon their bodies, which stresses their muscles, joints and bones to the limit. Sports physiotherapists help athletes recover from sporting injuries and provide education and resources to prevent problems. Each sports physiotherapist usually has sport-specific knowledge that addresses acute, chronic and overuse injuries. Their services are generally available to sportsmen and women of all ages engaged in sports at any level of competition.
Members of Sports Physiotherapy Australia (SPA) have experience and knowledge of the latest evidence-based practice, professional assessment and diagnosis of sports injuries, and effective hands-on management techniques and exercise protocols to assist recovery and prevent future damage. SPA members have access to the most recent advances in sports physiotherapy. You'll be pleased to know that most PhysioWorks physiotherapists and massage therapists are particularly interested in sports injury management.
General Sports Physio FAQs
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Acute Sports Injury Clinics
- Sports Physiotherapy Treatment
- Youth Sports Injuries
Injury Management
- Sports Injury? What to do? When?
- When Can You Back to Sport?
- Sports-Related Injuries
- Knee Sports Injuries
- Sports Health Conditions
Sports Massage
Sports Insurance
Related Articles
- Sports Injury Management: This article provides a comprehensive look at how sports injuries are managed, including prevention strategies and treatment options.
- Soft Tissue Injury Healing: Readers can learn about the healing process for soft tissue injuries, including practical advice for each phase of recovery.
- Prehabilitation: Key to Injury-Free Sports Performance: Offers insights into how athletes can prevent injuries before they occur, focusing on strengthening and conditioning practices.
- Athletics Injuries - Comprehensive Physio Guide: A detailed guide on common injuries in athletics and how to treat and prevent them, making it a valuable resource for athletes of all levels.
- Acute Sports Injury Clinic: Highlights the services offered by sports injury clinics, including fast-track assessments and treatments for acute sports injuries.
- Effective Management of Kids Sports Injuries: This guide focuses on the unique aspects of managing sports injuries in children, offering parents and coaches valuable advice on care and prevention.
More Information
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateCommon Muscle Injuries
A Physiotherapist's Guide
Introduction
Muscle injuries, presenting as muscle strain, pain or myalgia, are prevalent health issues affecting a wide range of individuals. This detailed guide, from a physiotherapist's perspective, delves into various muscle injuries, elaborating on their management, prevention, and the importance of professional advice. Explore the linked articles for an in-depth understanding of muscle injuries and their effective treatment.
Neck & Back Muscle Injuries: Causes and Solutions
- Back Muscle Pain: This pain often results from prolonged poor posture or physical overuse. Key to relief is engaging in exercises that strengthen the core muscles and improve posture, thereby alleviating the strain on the back.
- Neck Sprain: Caused by sudden, awkward movements, a neck sprain can benefit from a combination of gentle stretches and targeted strengthening exercises to restore flexibility and strength.
- Text Neck: A modern ailment resulting from extended mobile device use, text neck can lead to chronic pain. Regular breaks, posture-awareness, and neck-strengthening exercises are essential for prevention.
- Whiplash: Commonly occurring in car accidents, whiplash requires a careful approach including neck stabilisation exercises and controlled movement to encourage healing and prevent further injury.
Lower Limb Muscle Injuries: Understanding and Treating
- Hamstring Strain: Particularly common among athletes, particularly runners, this strain demands rest initially, followed by a carefully structured rehabilitation program focusing on gradual strength building and flexibility.
- Thigh Strain: Often seen in sports involving sprinting and jumping, thigh strains need a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) in the initial stages, followed by carefully planned strengthening exercises.
- Groin Strain: This injury requires a nuanced approach, including sufficient rest and targeted exercises, to ensure a safe and effective recovery.
- Calf Muscle Tear: Key to recovery is a balance of rest, gentle stretching exercises, and a gradual return to full activity, ensuring the muscle heals correctly and strength is regained.
Upper Limb Muscle Injuries: Prevention and Care
- Golfer's Elbow and Tennis Elbow: Both these conditions involve inflammation of the tendons and require a rest period, followed by ice therapy and specific exercises tailored to strengthen the affected muscles.
- Corked Thigh: Resulting from direct impacts, these injuries demand immediate application of ice and a controlled, gradual exercise regime for recovery.
- DOMS, Fatigue-Related Cramps & Myalgia: Adequate rest, good hydration, and gentle stretching are crucial in alleviating these conditions.
- RSI: Regular stretching, ergonomic workplace adjustments, and taking breaks are key preventive measures for repetitive strain injury.
Systemic Causes of Muscle Pain: A Holistic View
- Fibromyalgia: This complex condition demands a holistic treatment approach, including exercise routines, stress management techniques, and sometimes medication.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Effective management combines medication, gentle exercise, and regular physiotherapy sessions.
Prevention and Management Strategies
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain muscle strength and flexibility, reducing the risk of muscle injuries.
- Posture Improvement: Good posture, both in motion and at rest, is crucial for preventing muscle strain.
- Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Adequate warm-up before and cool-down after physical activity is vital in preventing muscle strains and injuries.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Making ergonomic adjustments at work and during daily activities can significantly reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries and other muscle-related issues.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Keeping a healthy weight reduces the strain on muscles, particularly in weight-bearing joints.
What to Do? Seeking Professional Advice
Consult a physiotherapist or doctor for personalised advice and treatment plans. Remember, early intervention can significantly improve recovery outcomes and prevent chronic problems.
Conclusion
While muscle injuries are common, effective management and prevention are achievable with the right approach and knowledge. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and various treatments available empowers individuals to take proactive steps in their recovery and prevention. For the most tailored and effective treatment, always seek the guidance of a professional physiotherapist.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateCommon Ligament Injuries


Ligament Injury
Ligament injuries frequently occur in various body parts, leading to pain and restricted movement. The most common sites include the knee, ankle, shoulder, wrist, hand, and spine.
Notably, knee injuries like ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL sprains are prevalent.
Shoulder injuries often involve the AC joint, while wrist and hand issues can include thumb and finger sprains.
Spinal ligament injuries, such as back and neck sprains, and whiplash, are also significant. Understanding these injuries helps in prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.
- Ankle Ligament Injuries
- Knee Ligament Injuries
- Shoulder Ligament Injuries
- Wrist & Hand Ligament Injuries
- Spinal Ligament Injuries
Ankle Ligament Injuries
Ankle injuries often result from sudden twists or rolls, leading to sprains and strains.
Knee Ligament Injuries
Knee ligament injuries are among the most common and can severely impact mobility and quality of life.
- ACL Injury
- PCL Injury
- MCL Sprain
- LCL Sprain
- Posterolateral Corner Injury
- Patella Dislocation
- Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprain
Shoulder Ligament Injuries
Shoulder ligament injuries can be debilitating, affecting a range of movements.
Wrist & Hand Ligament Injuries
Injuries in the wrist and hand are common, especially in sports and physical activities.
Spinal Ligament Injuries
Spinal ligament injuries can result from various causes, including posture issues and physical impacts.
Related Articles
- Ligament Tear - Common Ligament Injuries: Offers a comprehensive overview of ligament injuries across different body parts, including prevention, early detection, and effective treatment strategies.
- Knee Ligament Injury - A Physiotherapist's Guide & Tips: Provides insights into diagnosing knee pain, covering ligament issues among other concerns, and suggests pain relief methods through exercise and treatment.
- Common Ankle Ligament Injuries: A Physiotherapist's Guide: Discusses the treatment and prevention strategies for ankle ligament injuries, emphasising the importance of early intervention.
- Sprained Ankle Treatment & Recovery Guide: Offers detailed guidance on the recovery timelines for sprained ankles, highlighting the importance of restoring strength, motion, and function for a full recovery.
- Ankle Strapping: Complete Guide To Injury Prevention: Focuses on preventing ankle injuries through effective strapping techniques and discusses conditions like ankle arthritis and biomechanical issues.
- Sub-Acute Soft Tissue Injury: Explores the treatment and recovery process for various ligament injuries, including those affecting the knee, shoulder, wrist, hand, and spine.
- Sprained Thumb Treatment And Recovery Tips: Delivers practical tips for treating and recovering from a sprained thumb, along with general management strategies for wrist and hand pain.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateCommon Tendinopathies
An Overview of Tendon Injuries
Tendinopathies affect individuals across various age groups and physical activities, and these prevalent musculoskeletal conditions cause pain and impaired function, significantly impacting the quality of life. Active individuals, including athletes and those engaged in repetitive occupational tasks, are particularly susceptible to these overuse injuries.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of common tendinopathies, focusing on their specific manifestations and management approaches. By exploring the intricate details of conditions ranging from Achilles Tendinopathy to de Quervain's Tenosynovitis, we aim to enhance understanding and promote effective treatment strategies for those affected.
Tendinitis vs Tendinopathy
It's important to note that "tendinitis" is often used interchangeably with tendinopathy, but the suffix "-itis" implies inflammation, which is not always present in tendinopathies. In many cases, the condition involves degeneration of the tendon rather than acute inflammation. As a result, the more accurate term used nowadays is "tendinopathy."
Tendinopathy Treatments
Treatment approaches for tendinopathies typically focus on managing pain, promoting healing, and addressing contributing factors (e.g., overuse, improper biomechanics). Additionally, treatment approaches have advanced to include more targeted therapies, such as eccentric exercises, physiotherapy, and sometimes regenerative medicine techniques, depending on the specific type and severity of the tendinopathy.
Tendinopathy Classifications
Tendinopathy classifications have evolved to encompass a more nuanced understanding of these conditions. The modern tendinopathy classifications now include the following:
- Tendinitis or Tendonitis is an acute tendon inflammation, usually resulting from overuse, injury, or repetitive strain. It involves the active inflammatory process, and the symptoms can include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- Tendinosis is a chronic degenerative condition of the tendon that occurs when repetitive micro-injuries do not have sufficient time to heal and repair properly. Unlike tendinitis, tendinosis does not primarily involve active inflammation. Instead, it is associated with a breakdown of collagen fibres within the tendon, leading to its structure and composition changes.
- Paratendonitis and Tenosynovitis: These conditions involve inflammation or irritation of the paratendon (the outer layer of the tendon) or the tenosynovium (the sheath surrounding certain tendons). Paratendonitis and tenosynovitis can lead to pain and limited function of the affected tendon and are often associated with repetitive motions or friction.
- Insertional Tendinopathy: This type of tendinopathy occurs at the point where the tendon attaches to the bone (the insertion site). It can involve inflammation, degeneration, or a combination of both at the tendon-bone interface.
- Mid-Substance Tendinopathy: Mid-substance tendinopathy refers to conditions affecting the central portion of the tendon rather than the attachment points. This tendinopathy is often related to chronic overuse and may involve changes in the tendon's structure without significant inflammation.
It's important to note that the classification and understanding of tendinopathies continue to evolve with ongoing research. If you suspect you have tendinopathy, it's best to seek evaluation and advice from a healthcare professional, such as your physiotherapist, who is experienced in tendon conditions.
Seeking Professional Advice
Consult a physiotherapist with a special interest in tendinopathies for personalised advice and treatment.
Specific Tendinopathies
Foot & Ankle
- Achilles Tendinopathy
- Achilles Tendon Rupture
- FHL Tendinopathy
- Peroneal Tendinopathy
- Tibialis Posterior Tendinopathy
Knee
Hip & Groin
Shoulder
Elbow
Wrist & Hand
Conclusion
Tendinopathy is a complex condition requiring careful diagnosis, treatment, and management. Understanding its phases, symptoms, and treatment options is vital for effective recovery.
What to Do?
If you suspect tendinopathy, consult a physiotherapist for a thorough assessment and tailored treatment plan. Remember, early intervention can significantly improve your prognosis and hasten recovery.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateRelated Articles
- Tendinopathy: Causes, Symptoms, And Effective Treatments - Discover a broad overview of tendinopathies, including causes, symptoms, and a variety of effective treatment options.
- Effective Tendinopathy Physiotherapy Treatment Strategies - Explore advanced physiotherapy treatment strategies for managing tendinopathies effectively.
- Biceps Tendinopathy: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments - Gain insights into the specific causes, symptoms, and treatment options for biceps tendinopathy.
- Gluteal Tendinopathy: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment - Learn about gluteal tendinopathy, its impact, causes, symptoms, and how it can be treated.
- Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy - Understand the specifics of rotator cuff tendinopathy, including its causes, symptoms, and various treatment methods.
- Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy - Find detailed information on proximal hamstring tendinopathy, including prevention and treatment strategies.
- Peroneal Tendinopathy - We discuss the causes, symptoms, and rehabilitation processes for peroneal tendinopathy, and how to return to sports safely.
- Wrist Tendinopathy - Uncover the range of treatment options for wrist tendinopathy, from early injury treatment to physiotherapy modalities.
- Hip Adductor Tendinopathy - Effective Physio Solutions - Explore the causes, symptoms, and physiotherapy solutions for hip adductor tendinopathy.












































































