Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Article by John Miller

Osgood-Schlatter Disease
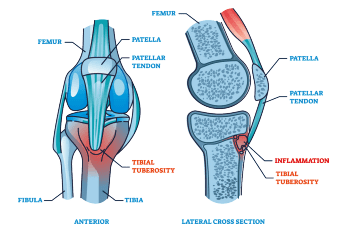
Osgood-Schlatter Disease, also recognised as tibial tuberosity apophysitis, affects adolescents experiencing growth spurts. It manifests as inflammation at the growth plate of the tibial tuberosity, where the patella tendon links to the shinbone. Unlike sudden injuries, Osgood-Schlatter Disease stems from overuse, especially in sports.
Recognising the Symptoms
Adolescents might feel pain and tenderness at the tibial tuberosity, exacerbated by activities like running, jumping, or even kneeling. Symptoms may include swelling in the area, quadriceps weakness, and in some cases, a visible lump. Around 20-30% may experience these symptoms in both knees. See more: Adolescent Leg Injuries.
The Root Causes
The condition occurs when repetitive movements strain the developing tibial tuberosity. During growth, the tibial tuberosity progresses from cartilage to bone, becoming vulnerable to injury in the apophyseal stage. The quadriceps muscle’s pull can outpace the bone’s ability to cope, leading to the characteristic pain of Osgood-Schlatter.
Who’s at Risk?
Osgood-Schlatter’s often targets boys aged 11-15 and girls 8-13, particularly those engaged in physical activities that involve extensive use of the quadriceps. Activities like basketball, netball, football, running and gymnastics are common culprits.
Diagnosis: A Simple Process
Typically, a clinical evaluation is sufficient to diagnose Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease. However, X-rays or MRI scans can rule out other conditions or confirm the diagnosis if needed.
Symptom Management and Progression
While some may see quick relief, others with severe symptoms need careful management to prevent long-term damage to the growth plate. Chronic cases might lead to complications, making walking or running difficult.
Physiotherapy: The First Line of Defence
Most patients with Osgood-Schlatter Disease see improvement with physiotherapy, which can include various treatments.
Physiotherapy emerges as a crucial ally for those battling Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease, with a striking 90%+ success rate reported for non-surgical treatment methods. Typically, symptoms fluctuate over a 12 to 24-month span before full recovery is seen. The secret to to improve the adolescent’s active symptoms.
Shielding the Knee
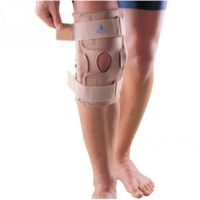
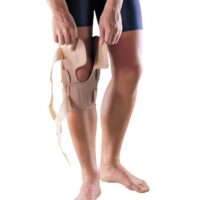
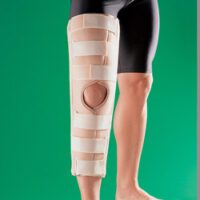
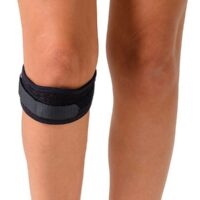
At the onset of symptoms, it’s vital to immediately minimise activities that place heavy stress on the knees, such as jumping and running. Utilising an infrapatellar strap can effectively redistribute stress away from the affected area. Kinesiology tape also offers pain relief and lessens the load at the tender site. In extreme cases, crutches might be recommended, but always seek personalised advice from a physiotherapist regarding knee care.
Combating Inflammation
Ice packs and TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) units can be powerful tools in reducing pain, often speeding up the return to sports. Applying ice is particularly beneficial post-exercise or while at home.
Nurturing Through Functional Training
Taking adequate rest is paramount in managing both the disease and associated pain. The decision to continue sports hinges on the severity of symptoms; hence, tailor your training load in consultation with a physiotherapist to ensure a safe and effective return to sports.
Therapeutic Exercises: Stretching, Massage & Foam Rollers
Tightness in the quadriceps, ITB, hamstrings, hip flexors, and calf muscles frequently contributes to the development of Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease. While your physiotherapist will recommend specific stretches, combining these with foam rolling and massage often yields superior results, particularly when stretches alone may exacerbate pain at the injury site.
Strengthening Strategies
To alleviate symptoms during the active phase of the disease, physiotherapists will tailor exercises to improve kneecap control and overall leg strength.
Support from Foot Arch Control & Orthotics
Inadequate foot biomechanics can intensify knee stress, thus exercises that bolster dynamic foot control are crucial. In certain cases, orthotics may be beneficial to counteract torsional stresses leading to knee injuries. However, consult with a physiotherapist or podiatrist, as opinions on their effectiveness vary, especially during the growth phases in adolescents.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease is self-limiting, resolving with the maturation of the tibial growth plate. Some may experience discomfort during activities like kneeling, especially if there’s an enlargement due to the condition. The aim is to prevent permanent bone protrusion.
Despite the possibility of prolonged symptoms, the vast majority find relief through conservative treatment, and surgery is rarely a consideration.
Conclusion: Seek Professional Guidance
While Osgood-Schlatter Disease can be a challenging journey, it’s not one to travel alone. For tailored treatment and the best outcomes, professional advice from a dedicated youth knee physiotherapist is indispensable. They’ll guide you through recovery with personalised care, ensuring you’re on the path to returning to the activities you love.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateRelated Articles
- Kids Sports Injuries – Provides a broad overview of common sports-related injuries in children, emphasising prevention and proper treatment.
- Sinding-Larsen-Johansson Disease – Delivers insights into a condition causing pain at the lower part of the kneecap, common in young athletes.
- Chondromalacia Patella – Discusses this condition related to the deterioration of the cartilage under the kneecap, including symptoms and treatment options.
- Patellar Tendinopathy (Jumper’s Knee) – Focuses on this specific injury, its causes, symptoms, and physiotherapy treatments.
- Youth ACL Injuries – Offers comprehensive information on ACL injuries specific to young athletes, including diagnosis and treatment options.
- Avulsion Fractures – Explains avulsion fractures, where a piece of bone is pulled off by a tendon or ligament, often occurring in active children and adolescents.
- Kids Spinal Pain – Provides an in-depth look at spinal pain in children, covering common causes and the role of physiotherapy in treatment and management.
- Juvenile Osteochondritis Dissecans – This article offers an understanding of a significant but less common condition that affects the joints of children and adolescents.