Mastitis - Blocked Milk Ducts
Article by Nadine Stewart

Mastitis Explained
Mastitis and Its Impact
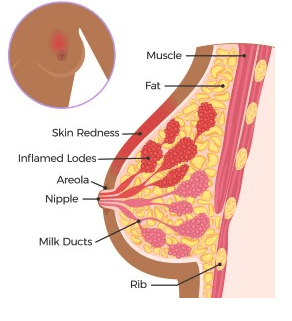
Mastitis, an inflammatory condition affecting breast tissue, often arises from blocked milk ducts. This blockage typically occurs when breast milk doesn’t drain effectively, leading to a buildup that clogs the ducts. While most common among breastfeeding mothers in the first six months post-birth or during weaning, mastitis can also occur during pregnancy and in non-breastfeeding women.
Recognising Mastitis Symptoms
Mastitis presents several distinct symptoms, such as:
- Noticeable hardening of the breast tissue
- Visible redness on the breast skin
- Flu-like symptoms, including fever and body aches
These signs can develop rapidly, often within 24 to 48 hours.
Causes and Prevention of Mastitis
Factors contributing to mastitis include:
- Skipped or rushed breastfeeding sessions
- Nipple injury
- Poor baby latch
- Stress and insufficient sleep
- Tight clothing and poorly fitting bras
- Previous breast engorgement or blocked ducts
Differentiating between mastitis and a simple blocked duct is vital, as blocked ducts typically do not require antibiotic treatment.
Blocked or Plugged Ducts
A plugged duct is marked by a painful, swollen lump in the breast, usually less severe than mastitis. These typically resolve independently within a day or two.
The Phenomenon of Breast Engorgement
Engorgement occurs when breasts become excessively full, either due to a sudden increase in milk production or overproduction. This often happens in the first week post-birth or during major changes in breastfeeding routines.
Symptoms of engorgement include:
- Swollen, tight, hard, and shiny breasts
- Pain and tenderness
- Flattened nipples due to swelling
These symptoms can worsen quickly, often in under two days.
Diagnosing Mastitis vs. Blocked Ducts
While mastitis and a blocked duct share similarities, distinguishing between them is essential. Mastitis is more likely if symptoms include fever, increased pain, and pronounced redness. If a blocked duct doesn’t clear, it can progress to mastitis.
Recent Research and Physiotherapy Treatment Options
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of physiotherapy in treating mastitis and blocked ducts. Key treatment methods include:
- Continuing breastfeeding or milk expression
- Positional feeding to aid drainage
- Applying heat pre- and post-feeding
- Using ice packs to reduce post-feeding inflammation
- Gentle self-massage
- Ensuring rest and hydration
- Employing therapeutic ultrasound and kinesiology taping
- Gentle stretches and breathing exercises for relaxation
Mastitis Therapeutic Ultrasound Treatment
Therapeutic ultrasound is particularly beneficial for persistent blocked ducts, often clearing them within one to two sessions.
Additional Treatment Considerations
Consulting a healthcare provider is crucial. Mastitis may require antibiotics, and imaging might be necessary to exclude an abscess. Probiotics can be helpful but should be discussed with a doctor.
A lactation consultant can offer valuable support, especially for latching issues, providing knowledge and practical aid.
Physiotherapists, like those at PhysioWorks, can guide and manage these conditions effectively with treatments like therapeutic ultrasound.
Conclusion
Empowering Mothers through Knowledge and Support
Mastitis and blocked ducts pose significant challenges for breastfeeding mothers, affecting their physical and emotional health. Prompt recognition of symptoms, understanding of underlying causes, and appropriate treatment are crucial for recovery. With healthcare guidance and physiotherapy interventions, mothers can effectively manage these conditions. Early action and informed choices are key.
For more information or to explore therapeutic ultrasound options, contact your physiotherapist at PhysioWorks for tailored advice and support.
Related Articles
- Understanding Rectus Diastasis and Recovery Strategies
Discover how physiotherapy can help in managing and recovering from rectus diastasis, improving core strength and stability post-pregnancy. - The Benefits of Therapeutic Ultrasound in Physiotherapy
Learn about how therapeutic ultrasound can enhance healing for a variety of conditions, from mastitis to muscle strains, through non-invasive treatment. - Choosing the Right Pregnancy Belly Band for Support
Explore the benefits of using a pregnancy belly band to alleviate discomfort and support your abdomen and lower back during pregnancy. - Safe Pregnancy Exercises for Every Trimester
Find out which exercises are recommended during pregnancy to maintain strength, flexibility, and reduce discomfort, with expert guidance from physiotherapists. - Managing Pregnancy Back Pain: Effective Strategies
Gain insights into physiotherapy techniques and practical tips to relieve back pain during pregnancy, enhancing your comfort and mobility. - SIJ Pain Relief During and After Pregnancy
Understand sacroiliac joint pain’s causes and treatment options, including exercises and manual therapy, to ease pelvic discomfort.
















































































