Spondylolisthesis
Article by John Miller
Spondylolisthesis
What is Spondylolisthesis?
Spondylolisthesis, a condition where one vertebral body slips forward over the one below, often results from structural changes, degenerative processes, or fractures within the spine. This slippage may arise from either isthmic or degenerative causes, with the former typically seen in younger individuals and the latter more prevalent as we age.
What Triggers Spondylolisthesis?
The two primary culprits behind spondylolisthesis are isthmic changes, which usually affect pre-teens and adolescents, and degenerative shifts that become more common with ageing. Isthmic spondylolisthesis often links to sports that involve intense back extension and rotation, leading to stress fractures that precede the condition.
Conversely, degenerative spondylolisthesis stems from the wear and tear of spinal segments, escalating to conditions like degenerative disc disease. Notably, a staggering 75% of spondylolisthesis cases occur at the L5-S1 level, indicating a common site for this condition.
Identifying the Symptoms
Symptoms vary from back and leg pain to neurological issues such as numbness or sciatica. Notable postural changes, known as swayback, and a limping gait are also common indicators of this condition.
Diagnosing Spondylolisthesis
A thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs are essential for diagnosing spondylolisthesis and determining its severity.
Treatment Approaches for Spondylolisthesis
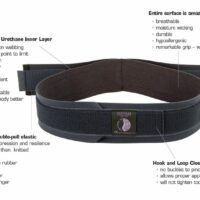
Initial treatment typically involves non-surgical methods, focusing on physiotherapy and lifestyle modifications. Exercises to strengthen the spine and alleviate symptoms are highly beneficial, with studies showing significant improvements in those following a customised exercise regimen.
Customised Physiotherapy for Rehabilitation
Physiotherapy is vital in managing spondylolisthesis, aiming to reduce pain and enhance spinal stability. Therapists utilise various techniques to alleviate discomfort, diminish muscle spasms, and bolster the spinal support structure.
Surgical Options
Surgery may be an option for those with severe symptoms or neurological impairment when conservative treatments are ineffective. Procedures like spinal fusion or decompression should be thoroughly discussed with a spinal specialist.
What Happens if Spondylolisthesis is Left Untreated?
If spondylolisthesis is left untreated, it can lead to a range of complications, potentially worsening the patient’s quality of life. Here’s what might happen:
- Increased Pain: Without treatment, the pain associated with spondylolisthesis, both in the back and potentially radiating down the legs (sciatica), may worsen over time.
- Progressive Slippage: The vertebral displacement can progress, leading to increased instability and deformity in the spine. This can further exacerbate pain and functional limitations.
- Neurological Symptoms: As the condition progresses, there’s a risk of nerve compression, which can result in numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and even bowel or bladder dysfunction in severe cases.
- Postural Changes: Advanced spondylolisthesis can lead to significant changes in posture, such as an exaggerated curve in the lower back (lordosis) or a forward-leaning posture, which can affect balance and mobility.
- Mobility Issues: Increased pain and decreased spinal stability can lead to difficulties with movement, affecting daily activities and reducing the individual’s overall mobility.
- Chronic Conditions: Over time, untreated spondylolisthesis may contribute to the development of chronic conditions such as chronic back pain and degenerative arthritis due to the ongoing stress and instability in the spine.
- Decreased Quality of Life: The cumulative effect of pain, mobility restrictions, and potential neurological symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, including their ability to work, engage in social activities, and maintain independence.
- Potential for Permanent Damage: In severe cases, prolonged nerve compression can lead to permanent nerve damage, which might not be fully reversible, even with treatment.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management, including physiotherapy, lifestyle modifications, and possibly surgery for severe cases, are crucial in preventing the progression of spondylolisthesis and avoiding these complications. Engaging with healthcare professionals early on allows for a tailored treatment plan that can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
Prognosis and Proactive Management
The outlook for individuals with spondylolisthesis is generally favourable, especially for low-grade cases. eg Grades I to II. Adherence to a comprehensive treatment plan is crucial for effective management. Grade III to V typically require surgical stabilisation, so please arrange an urgent appointment with your doctor.
Does Spondylolisthesis Heal on its Own?
Spondylolisthesis does not typically heal on its own. While the symptoms associated with spondylolisthesis, such as pain, may improve over time with non-surgical treatments like physiotherapy, lifestyle modifications, and pain management techniques, the underlying condition—the slippage of one vertebral body over another—generally remains. Non-surgical treatments can effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life, but they do not reverse the slippage.
In cases of spondylolisthesis caused by a bone fracture (isthmic spondylolisthesis), the fracture itself may heal over time, especially in younger individuals, but the vertebral slippage that has occurred as a result of the fracture may not correct itself without intervention.
Surgical treatments, such as spinal fusion, are sometimes recommended for severe cases of spondylolisthesis where there is significant slippage, intractable pain, or neurological symptoms that affect daily living. Surgery aims to stabilize the affected vertebrae and alleviate the symptoms by preventing further slippage.
It’s essential for individuals with spondylolisthesis to seek a professional medical evaluation to understand the severity of their condition and to receive a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific symptoms and needs. Regular monitoring and appropriate management can help prevent the condition from worsening and improve the individual’s overall functioning and quality of life.
How Do You Stop Spondylolisthesis from Progressing?
To prevent spondylolisthesis, or prevent it from progressing, it is important to maintain spinal health through regular exercise, correct posture, and avoiding excessive back strain. Athletes should be particularly mindful of their techniques and use appropriate support to reduce the risk of isthmic spondylolisthesis.
Conclusion
With an informed treatment plan and preventative measures, individuals with spondylolisthesis can effectively manage their condition. Early and consistent management is key to preventing progression and maintaining quality of life. Staying informed and collaborating with healthcare professionals can help those affected by spondylolisthesis lead active and fulfilling lives.
If you have a spondylolisthesis, it is strongly recommended that you seek the guidance of your back physiotherapist and/or spinal surgeon, so please book an appointment.
Related Articles
- Degenerative Disc Disease:
- Readers will learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for degenerative disc disease, which is closely linked to degenerative spondylolisthesis.
- Back Pain:
- This page offers insights into common causes of back pain, including spondylolisthesis, and outlines various treatment strategies.
- Core Stability Exercises:
- Here, readers can find exercises aimed at strengthening core muscles, which is crucial for managing spondylolisthesis and enhancing spinal stability.
- Sciatica:
- The article explains sciatica, a common symptom of spondylolisthesis, including causes, symptoms, and treatment methods.
- Posture Advice:
- Offers guidance on maintaining proper posture to prevent back pain and other spinal conditions, including spondylolisthesis.
- Sports Injuries:
- Explains how certain sports activities can lead to conditions like isthmic spondylolisthesis and the importance of proper technique and preventive strategies.
- Spondylolysis:
- Provides information on spondylolysis, a condition often associated with isthmic spondylolisthesis, including its diagnosis, treatment, and management.