Wrist & Hand Arthritis
Article by Shane Armfield

Wrist & Hand Arthritis
Your Guide to Relief and Recovery
Wrist and hand arthritis can be a significant challenge, particularly as we get older. It leads to the deterioration of wrsit and hand joints, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Osteoarthritis typically results from repetitive stress on the joints, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that erodes the joints.
What is the Average Age to Get Hand Arthritis?
The average age for developing hand arthritis can vary widely, as different forms of arthritis have different age ranges for onset. For example, rheumatoid arthritis often starts when a person is between 30 and 50 years old, but it can affect people of any age, including children in the form of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Osteoarthritis of the hands, a more degenerative form of the condition related to age and wear and tear, typically becomes more common as people reach their senior years. About half of all women and one-quarter of all men will experience symptoms of hand osteoarthritis by the time they are 85 years old.
Exercise: A Key to Managing Wrist & Hand Arthritis Pain
Research has shown that regular exercise is crucial in managing wrist and hand arthritis. It not only helps to alleviate discomfort but also strengthens joints and enhances flexibility. Simple exercises like wrist bends and finger stretches, especially when gradually intensified under a physiotherapist’s guidance, can be very beneficial.

Comprehensive Treatment Options
Several treatment strategies can help those battling wrist and hand arthritis:
- Gentle Passive Movement Techniques: A therapist can move the joints gently to improve mobility without causing pain.
- Heat and Electrical Treatments: Heat application reduces stiffness and pain, and TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) can aid in managing pain.
- Mobility and Strengthening Exercises: Custom exercises are designed to improve joint function and prevent further deterioration.
- Massage and Acupuncture: These therapies can relieve pain and enhance blood flow to the affected areas.
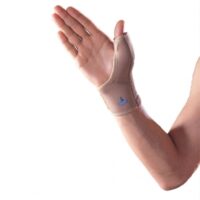
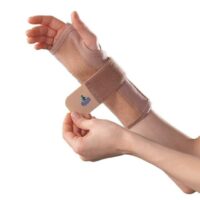
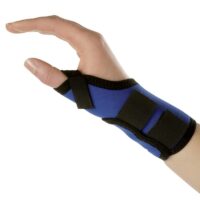
- Supportive Braces: Braces provide stability and can lessen pain during activities.
- Preventative Advice: Physiotherapists can offer tips on modifying activities and lifestyles to prevent further joint damage.
Empowering Your Wrist & Hand Mobility Journey
Living with wrist and hand arthritis can be daunting. However, the right combination of exercise, therapies, and lifestyle changes can significantly improve your symptoms and quality of life.
Navigating Common Concerns
- Treating wrsit and hand arthritis involves exercises, therapies such as heat treatment and acupuncture, and lifestyle adjustments.
- Stage 1 early arthritis in the hands is characterised by mild symptoms, including occasional pain and stiffness without significant impairment.
- Identifying hand arthritis can be done by noting symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion.
- Factors that make arthritis in the hands worse include repetitive joint stress, a poor diet, lack of exercise, and cold weather.
What Triggers Wrist & Hand Arthritis?
Wrist and hand arthritis can be triggered by several factors. Post-traumatic arthritis, a form of osteoarthritis, occurs after a joint injury, such as a fracture or ligament injury. It is particularly common in the wrist due to its complex structure and the lack of muscle or tendon attachments to the eight bones in the wrist, leaving it vulnerable to everyday wear and tear.
It can take years for arthritis to develop following an injury, with the condition being more prevalent in individuals aged 45 to 60 years. Other risk factors for hand or wrist arthritis include age, sex (with women being more at risk), obesity, genetic predisposition, joint issues such as infections or overuse, and injuries, even if they were properly treated at the time.
What to Do Next?
Addressing wrist and hand arthritis requires a comprehensive approach, focusing on treatment, exercise, and lifestyle modifications. By taking proactive steps and seeking professional guidance, managing arthritis becomes a more navigable journey, leading to improved mobility and a better quality of life.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of wrist and hand arthritis, the next step is to consult a professional. Seeking the advice of a physiotherapist is essential. They can create a personalised treatment plan and guide you through the appropriate exercises and therapies, ensuring you’re on the path to managing your condition effectively.
Rochedale - Call 38410277
Book Online: RochedaleSalisbury - Call 32751044
Book Online: SalisburySandgate - Call 32691122
Book Online: SandgateRelated Articles for Further Reading
- Effective Hand & Wrist Pain Treatment With Physiotherapy: Offers insights into managing hand and wrist pain, including treatments like joint mobilisation and soft tissue massage.
- Arthritis Overview: Provides a comprehensive look into arthritis, including definitions, symptoms, and treatments.
- Osteoarthritis Information: Discusses osteoarthritis specifics, its causes, risk factors, and management strategies.
- Wrist Fracture Recovery: Discusses recovery strategies for wrist fractures, which can be related due to similar treatment approaches like supportive braces and pain management.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Treatments: Though focused on carpal tunnel syndrome, it shares common treatment methodologies that could be beneficial for wrist and hand arthritis sufferers.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – Insights and Management: Explores rheumatoid arthritis, offering valuable information on autoimmune disorders that affect the joints, including the hands and wrists.