Article by Harry Lawrence
Recurrent Back Pain

Breaking the Cycle of Pain
Recurrent back pain often presents a persistent challenge, impacting work, leisure, and overall quality of life. Understanding the contributing factors and adopting effective management strategies are crucial steps towards breaking this cycle of pain and discomfort.
Recurrent Back Pain Incidence
A research study of 250 back pain suffers found that within 12 months after back pain recovery, 69% had a recurrence of an episode of low back pain. The median time to recurrence of an episode of low back pain was 139 days. Frequent exposure to awkward postures, longer time sitting (> 5 hours per day), and more than two previous episodes were predictive of recurrence episode. (da Silva et al 2019)
Understanding the Nature of Recurrent Low Back Pain
Characterised by episodes that reoccur over time, recurrent low back pain may initially stem from muscle strains or poor posture. However, its persistence often signals underlying issues such as muscle imbalances, age-related changes, or degenerative conditions.
A Physiotherapist's Approach to Assessment
A thorough assessment by a physiotherapist is the first step in addressing recurrent low back pain. This process typically includes an evaluation of your posture, movement, joint function, and muscle strength. In some instances, additional imaging like X-rays or MRIs may be necessary, but this is not always required.
Contemporary Pain Management Strategies
Pain management encompasses a range of strategies, from heat or cold therapy to over-the-counter medications. However, it's essential to consult with a spinal physiotherapist or doctor to determine the most suitable approach for your specific situation.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Relief
Adjusting your lifestyle can significantly reduce the recurrence of low back pain. This includes improving sleep quality, reducing prolonged sitting, and incorporating regular breaks into your daily routine.
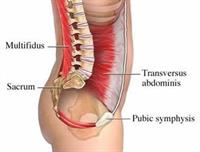
Back Exercise: The Key to Strengthening and Flexibility
Tailored exercise programs designed by physiotherapists can strengthen core muscles, enhance flexibility, and correct muscle imbalances. Consistency and adherence to these exercises are vital for long-term relief.
The Importance of Posture and Ergonomics
Poor posture is a common factor in recurrent low back pain. Making ergonomic adjustments at work and maintaining proper posture can significantly alleviate back strain.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Stress and anxiety can worsen low back pain. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises not only manage stress but also positively influence your overall experience of pain.
Weight Management: A Crucial Element
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential in managing recurrent low back pain, as excess weight adds extra strain on the spine. A balanced diet and regular physical activity are key components of effective weight management.
Regular Physical Activity for a Healthier Back
Incorporate activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling into your routine to improve overall fitness and spinal health. Choose exercises that are suitable for your specific condition.
Empowering Yourself Against Recurrent Back Pain
Overcoming recurrent low back pain requires a combination of professional guidance, targeted exercises, lifestyle changes, and stress management. Consistency and a commitment to long-term well-being are fundamental to success.
What to Do? Seek Professional Advice
If recurrent low back pain is affecting your life, consulting with a physiotherapist is a crucial step. Our physiotherapists at PhysioWorks can develop a personalised plan tailored to your unique needs and goals, guiding you towards long-term relief and improved quality of life.
Related Articles
- Lower Back Pain - Understanding & Managing - Physio Tips: Offers insights into the prevalence of low back pain and various treatment success stories. It emphasises the importance of seeking professional advice for musculoskeletal disorders.
- Back Pain Physiotherapy: Your Guide To What To Expect: Discusses the effectiveness of physiotherapy in managing back pain, covering treatments for disc-related injuries, back joint injuries, nerve-related injuries, pelvis-related injuries, and systemic diseases affecting the back.
- Core Stability Training For Effective Low Back Pain Relief: Highlights the benefits of core stability training in reducing low back pain, including a discussion on recent research and the importance of a personalised core stability program.
- Effective Back Exercises And Core Strength: Physio Insights: Provides information on exercises and core strength development for low back pain relief, emphasising the role of muscle injuries and core stability deficiency in causing pain.
- Back Pain Prevention: Essential Tips From A Physiotherapist: Focuses on the role of exercise combined with education in reducing the risk of low back pain episodes, showcasing PhysioWorks' approach to tailored exercise programs for flexibility, strengthening, and postural control.
- Pulled Back Muscle: Offers details on the terminology used to describe muscle and ligament injuries in the back, including diagnostic tools and treatment options.